Copyright
©The Author(s) 2002.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 15, 2002; 8(1): 108-113
Published online Feb 15, 2002. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i1.108
Published online Feb 15, 2002. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i1.108
Figure 1 Sequence of CD226 cDNA and primers.
174-923 bp: extracellular region of CD226; 174-227 bp: signal peptide sequence; 924-998 bp: transmembrane region; labeled sequence: primers; under-lined sequence was the splicing donor sequence.
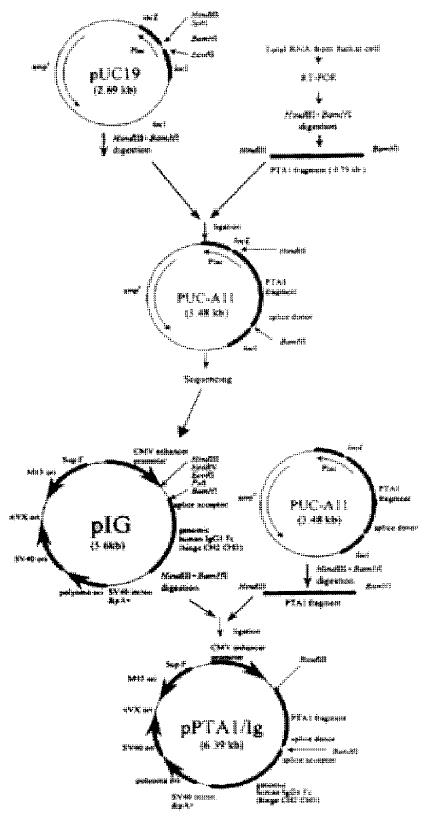
Figure 2 Construction of pCD226/Ig fusion vector.
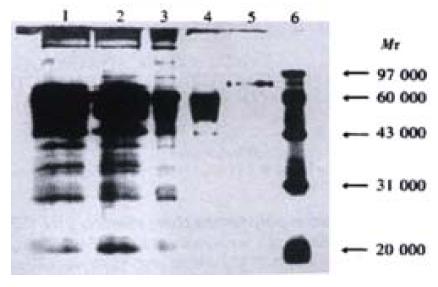
Figure 3 Identification of CD226/Ig fusion protein purified by Leo-A1 Sepharose-4B affinity column.
1. Supernatant of pIG vector transfected COS-7 cells; 2. Supernatant of pCD226/Ig transfected COS-7 cells; 3. Supernatant of pCD226/Ig trans-fected COS-7 cells after concentrated by ammonium sulfate; 4. Flow through solution of pCD226/Ig transfected COS-7 cells after affinity chromatography; 5. CD226/Ig fusion protein purified by Leo-A1 sepharose-4B affinity column; 6. Marker.
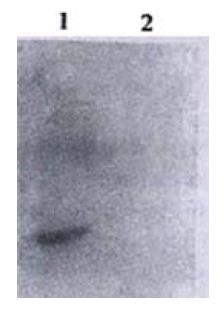
Figure 4 Western-blot result of CD226/Ig by anti-IgG polyclonal antibody Lane 1.
Supernatant of pCD226/Ig transfected COS-7 cells; Lane 2. Super-natant of pIG transfected COS-7 cells
Figure 5 CD226L expression on Colo205 cells identified by CD226/Ig immunohistochemistry.
A: Colo205 negative control (stained with hIg); B: Colo205 cells were specifically stained by CD226/Ig.
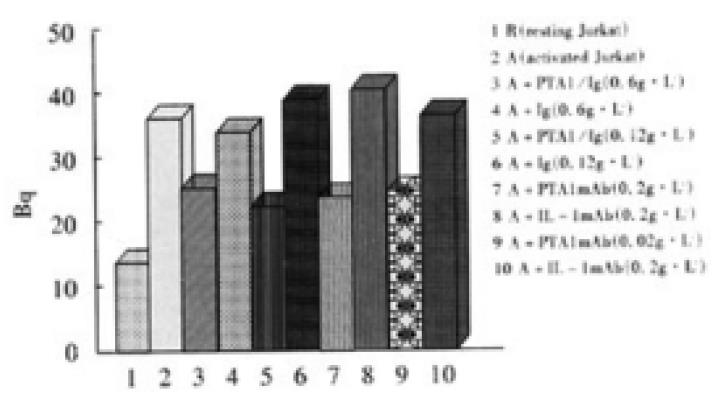
Figure 6 Adhesion experiments of activated Jurkat cells with Colo205 cells.
Density of Colo205 was 0.5 × 105 per well. Density of Jurkat was 1 × 105 per well. R stand for resting Jurkat cells. A stand for activated Jurkat cells.
- Citation: Sun K, Jin BQ, Feng Q, Zhu Y, Yang K, Liu XS, Dong BQ. Identification of CD226 ligand on colo205 cell surface. World J Gastroenterol 2002; 8(1): 108-113
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v8/i1/108.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v8.i1.108