Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2020; 26(30): 4501-4522
Published online Aug 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i30.4501
Published online Aug 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i30.4501
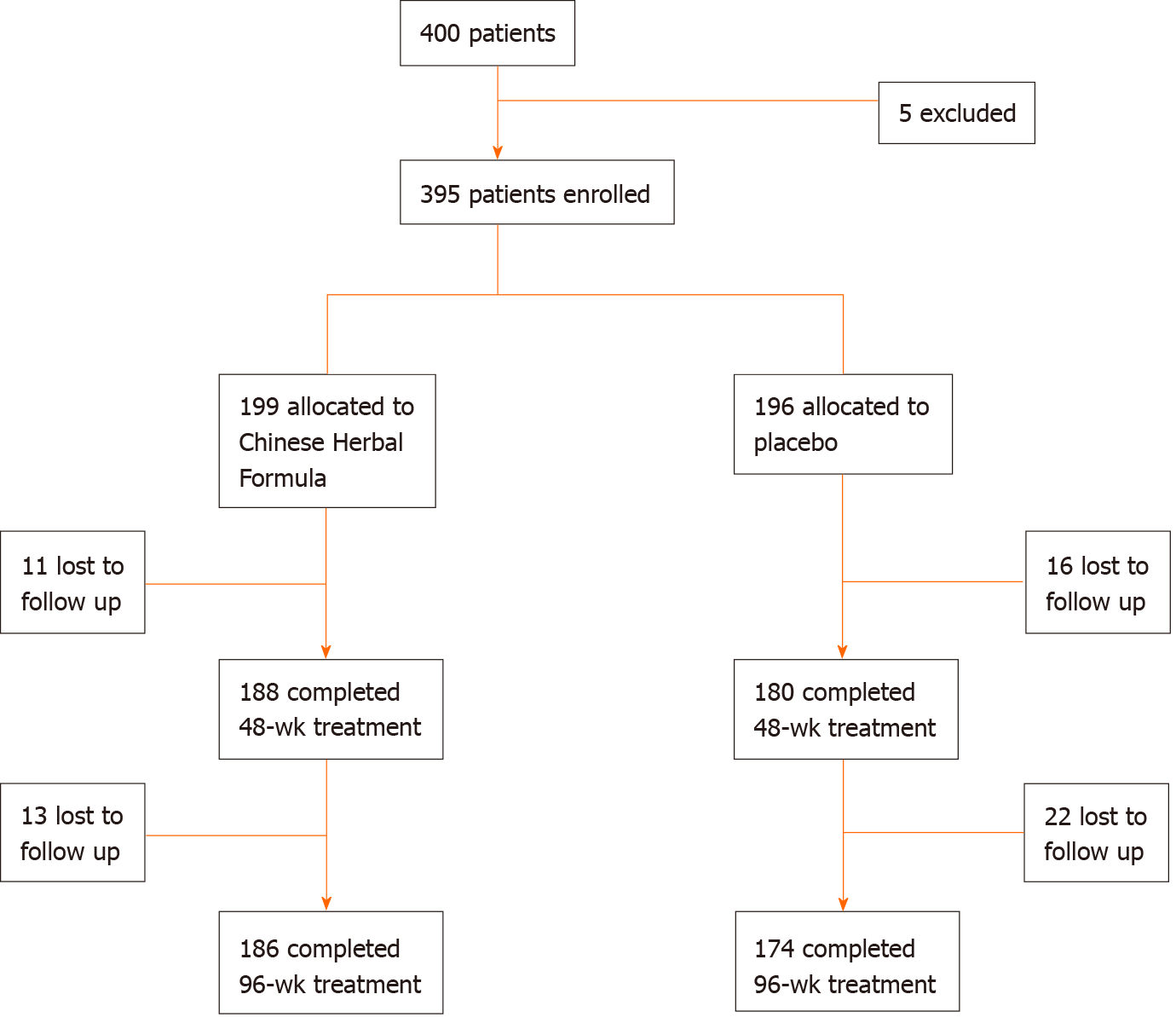
Figure 1 Study flowchart.
Figure 2 Concentration curves of hepatitis B virus surface antigen and hepatitis B e antigen levels during Chinese herbal formula and placebo treatment.
There was no significant difference between the two groups in serum hepatitis B virus surface antigen or hepatitis B e antigen levels at baseline. A: The patients in the treatment group showed significantly decreased hepatitis B virus surface antigen level in serum compared with those in the control group at weeks 48 and 96; B: The patients in the treatment group showed significantly decreased hepatitis B e antigen level in serum compared with those in the control group at weeks 48 and 96. Mann-Whitney U test. Treatment group: Chinese herbal formula invigorating kidney and clearing away the heat and expelling superficial evils; Control group: Placebo. HBeAg: Hepatitis B e antigen; HBsAg: Hepatitis B surface antigen; ICE: Invigorating kidney and clearing away the heat and expelling superficial evils.
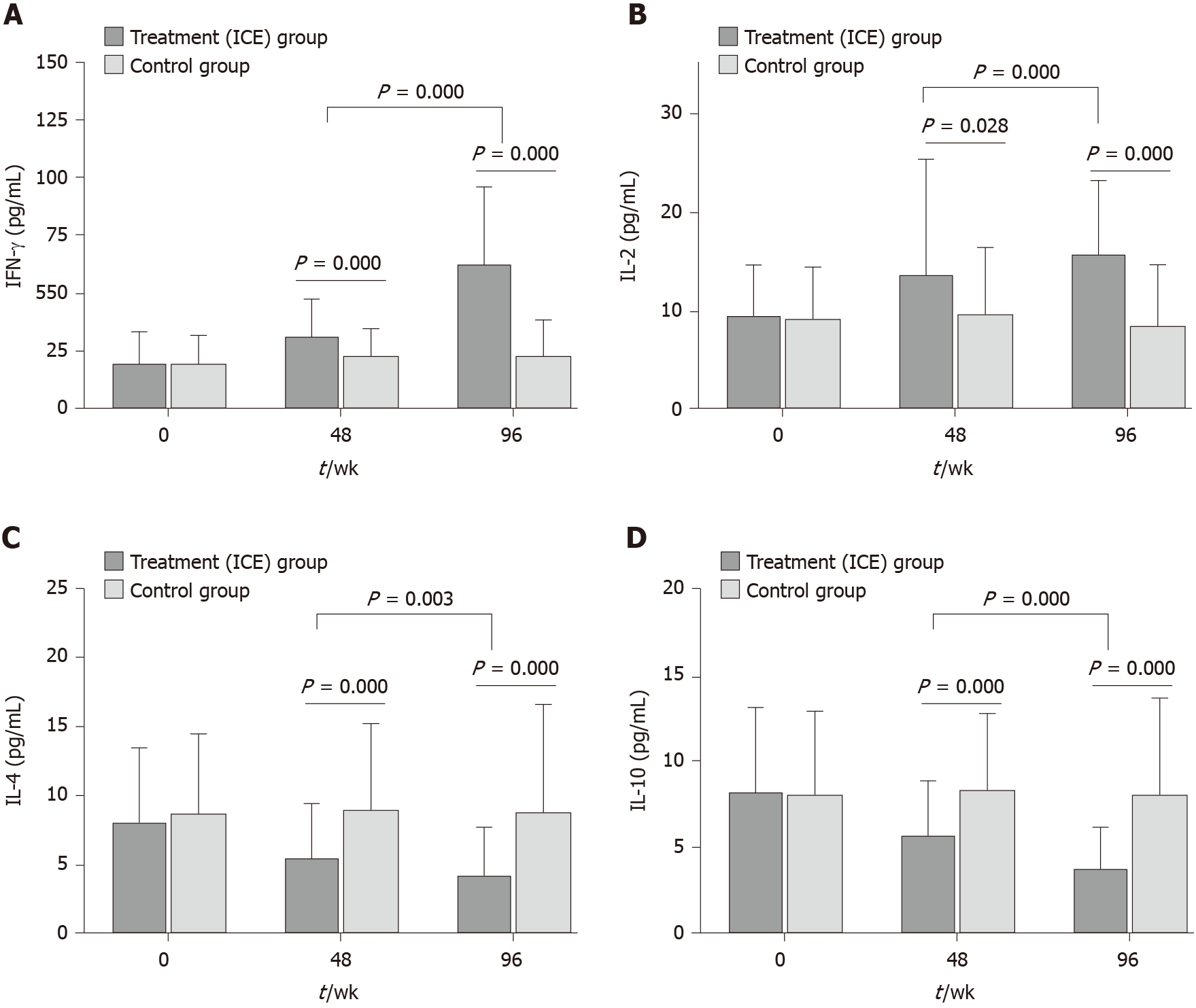
Figure 3 Serum levels of interferon-γ, interleukin-2, interleukin-4 and interleukin-10 were determined by ELISA.
A: The patients in the treatment group showed significantly increased interferon-γ levels in serum compared with the placebo group; B: The patients in the treatment group showed significantly increased interleukin (IL)-2 levels in serum compared with the placebo group; C: The patients in the treatment group showed significantly decreased IL-4 levels in serum compared with the placebo group; D: The patients in the treatment group showed significantly decreased IL-10 levels in serum compared with the placebo group. Serum levels of interferon-γ, IL-2, IL-4 and IL-10 were compared between the subgroup weeks 48 and 96. Mann-Whitney U test. Treatment group: Chinese herb formula invigorating kidney and clearing away the heat and expelling superficial evils; Control group: Placebo. IL: Interleukin; IFN-γ: interferon-γ; ICE: Invigorating kidney and clearing away the heat and expelling superficial evils.
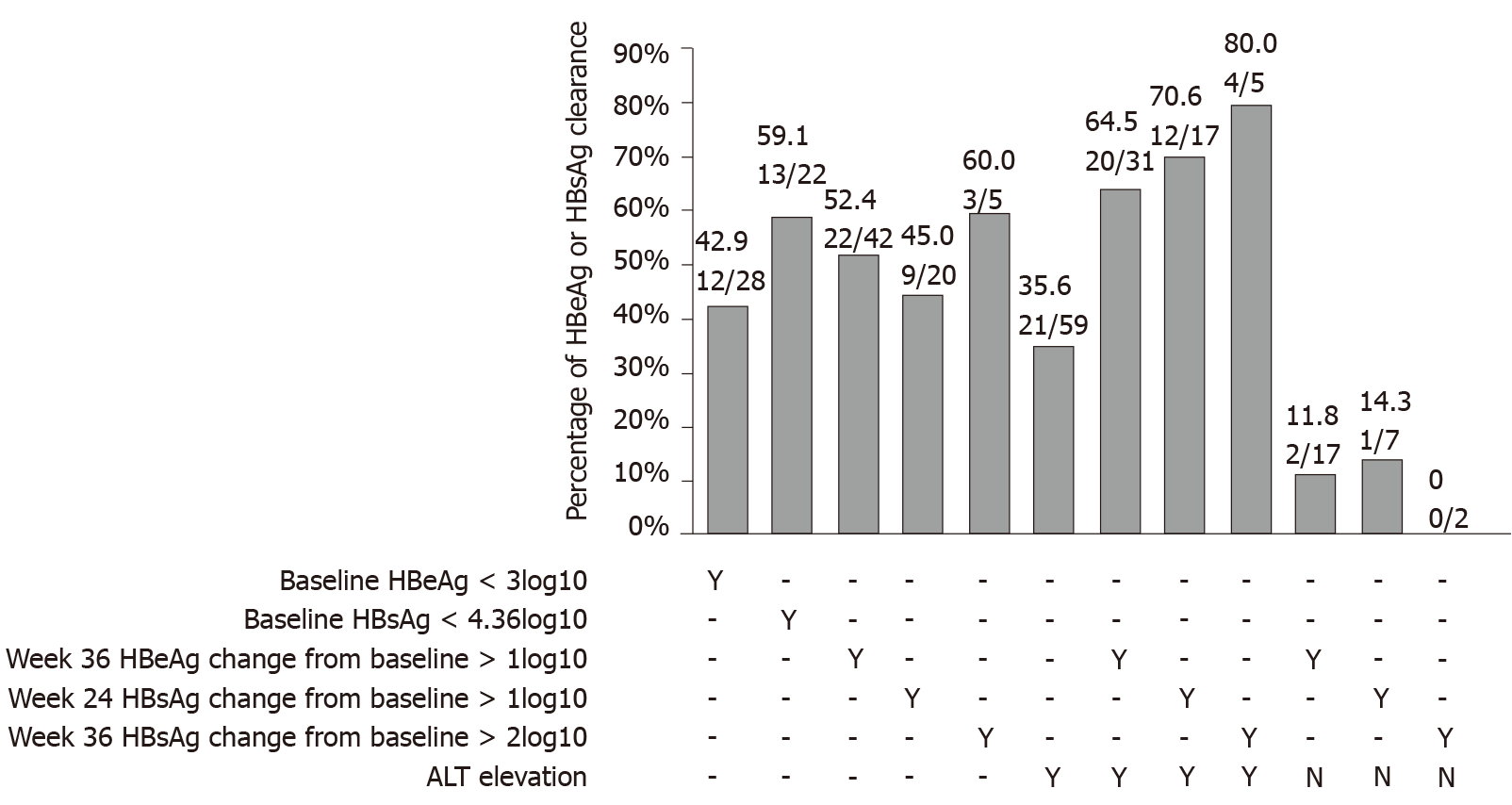
Figure 4 Percentage of hepatitis B virus surface antigen and hepatitis B e antigen clearance.
Percentage of hepatitis B virus surface antigen and hepatitis B e antigen clearance among patients stratified by baseline, week 24 and week 36 hepatitis B e antigen and hepatitis B virus surface antigen levels; week 36 hepatitis B e antigen change from baseline; weeks 24 and 36 hepatitis B virus surface antigen change from baseline; and week 24 alanine aminotransferase elevation. HBeAg: Hepatitis B e antigen; HBsAg: Hepatitis B surface antigen; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase.
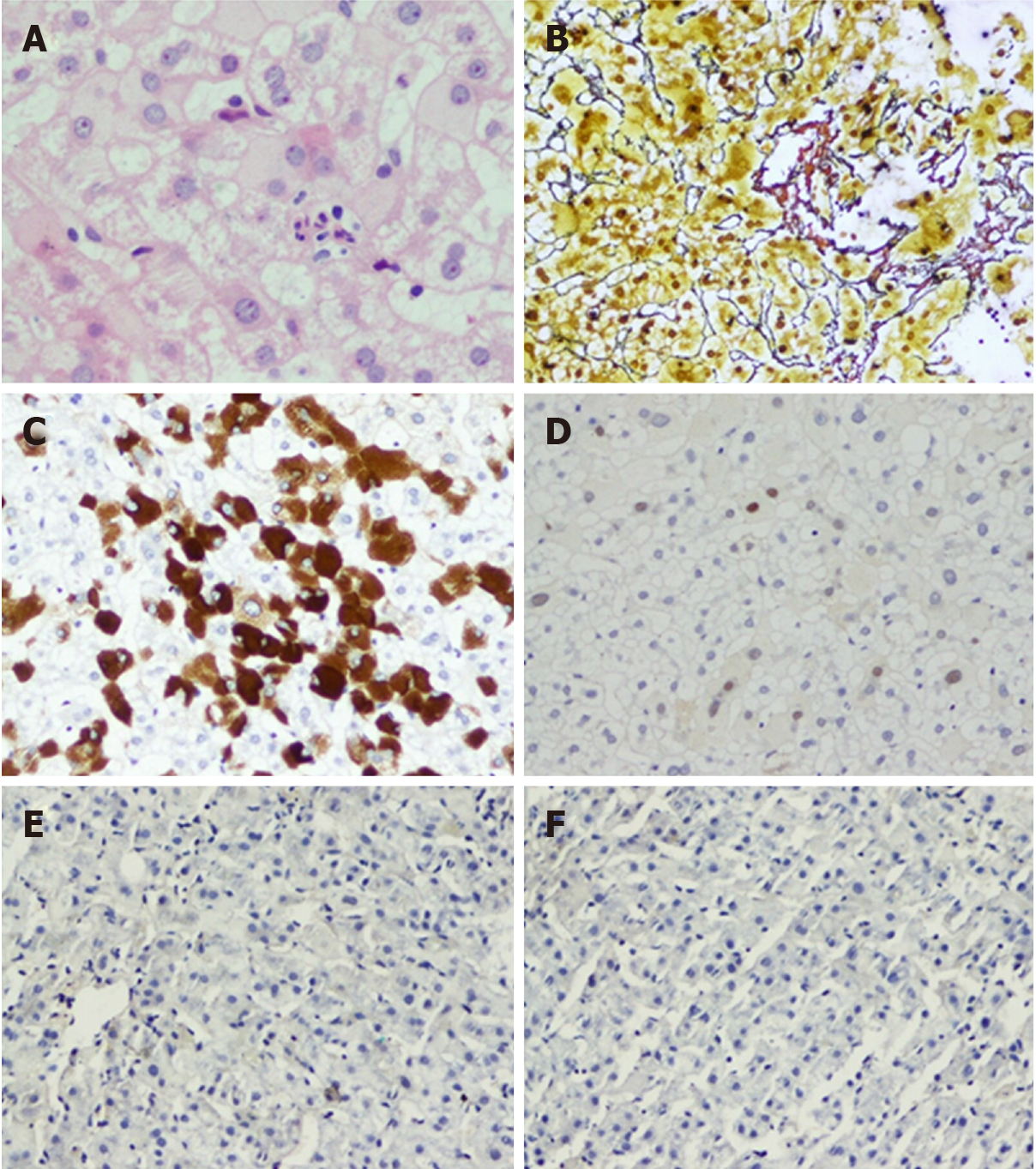
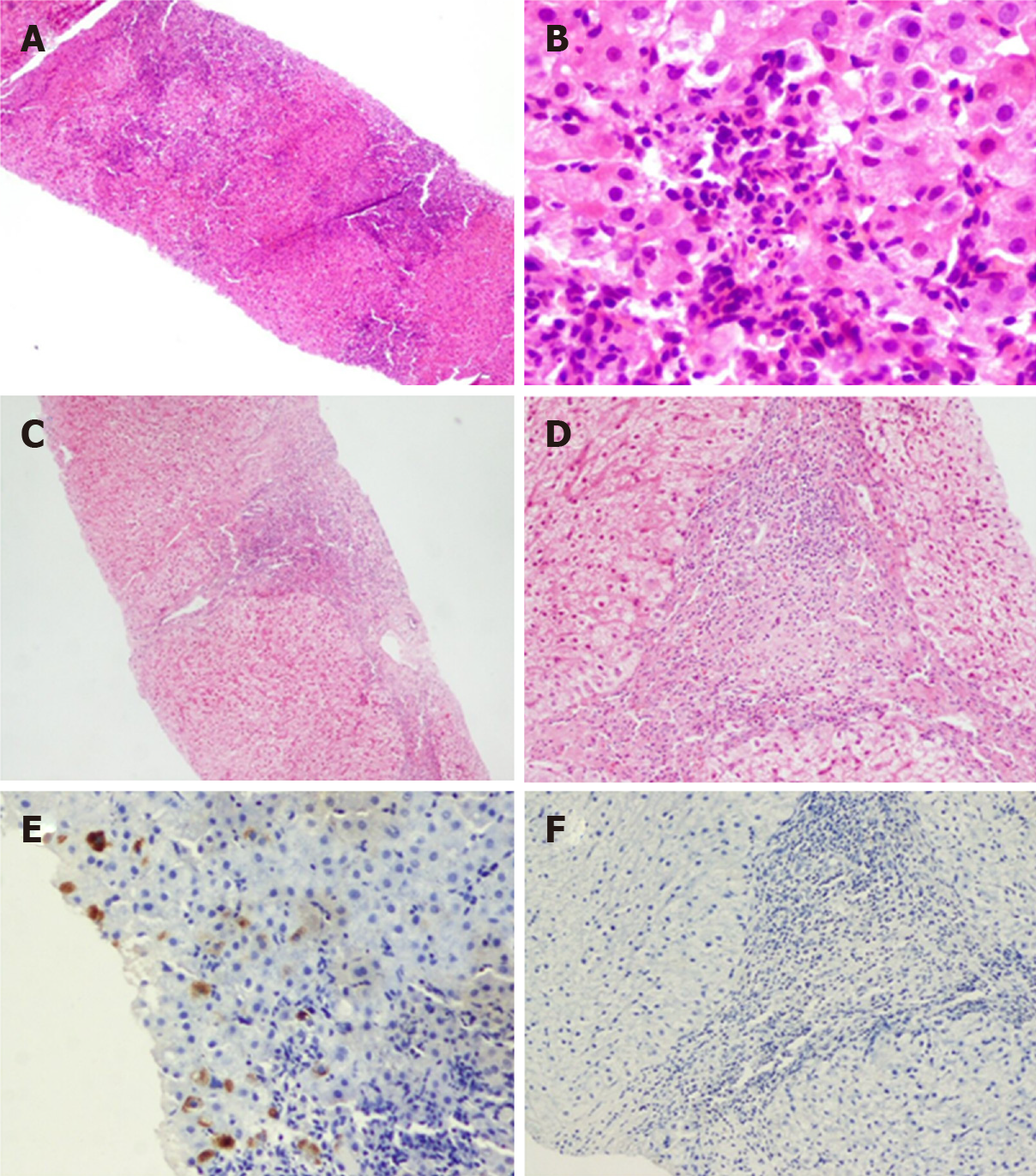
Figure 5 Typical case 1 (pathology No.
liver 0372). A: Focal necrosis in hepatic lobules with inflammatory cell infiltration (G1); B: Perisinusoidal fibrosis and lobular fibrosis (S1); C: Hepatitis B virus surface antigen (+++) in one immunohistochemistry assay of liver; D: Hepatitis B virus core antigen (+) in one immunohistochemistry assay of liver; E: Hepatitis B virus surface antigen (-) in two immunohistochemistry assays of liver; F: Hepatitis B virus core antigen (-) in two immunohistochemistry assays of liver.
Figure 6 Typical case 2 (pathology No.
liver 0178). A: Extensive necrosis involving multiple lobules and bridging necrosis at low magnification (G4); B: Necrotic cellular debris at high magnification (G4); C: Limited fusion necrosis in two immunohistochemistry assays of liver at low magnification (G3); D: Limited fusion necrosis in two immunohistochemistry assays of liver at high magnification (G3); E: Hepatitis B virus surface antigen (+) in one immunohistochemistry assay of liver; F: Hepatitis B virus surface antigen (-) in two immunohistochemistry assays of liver.
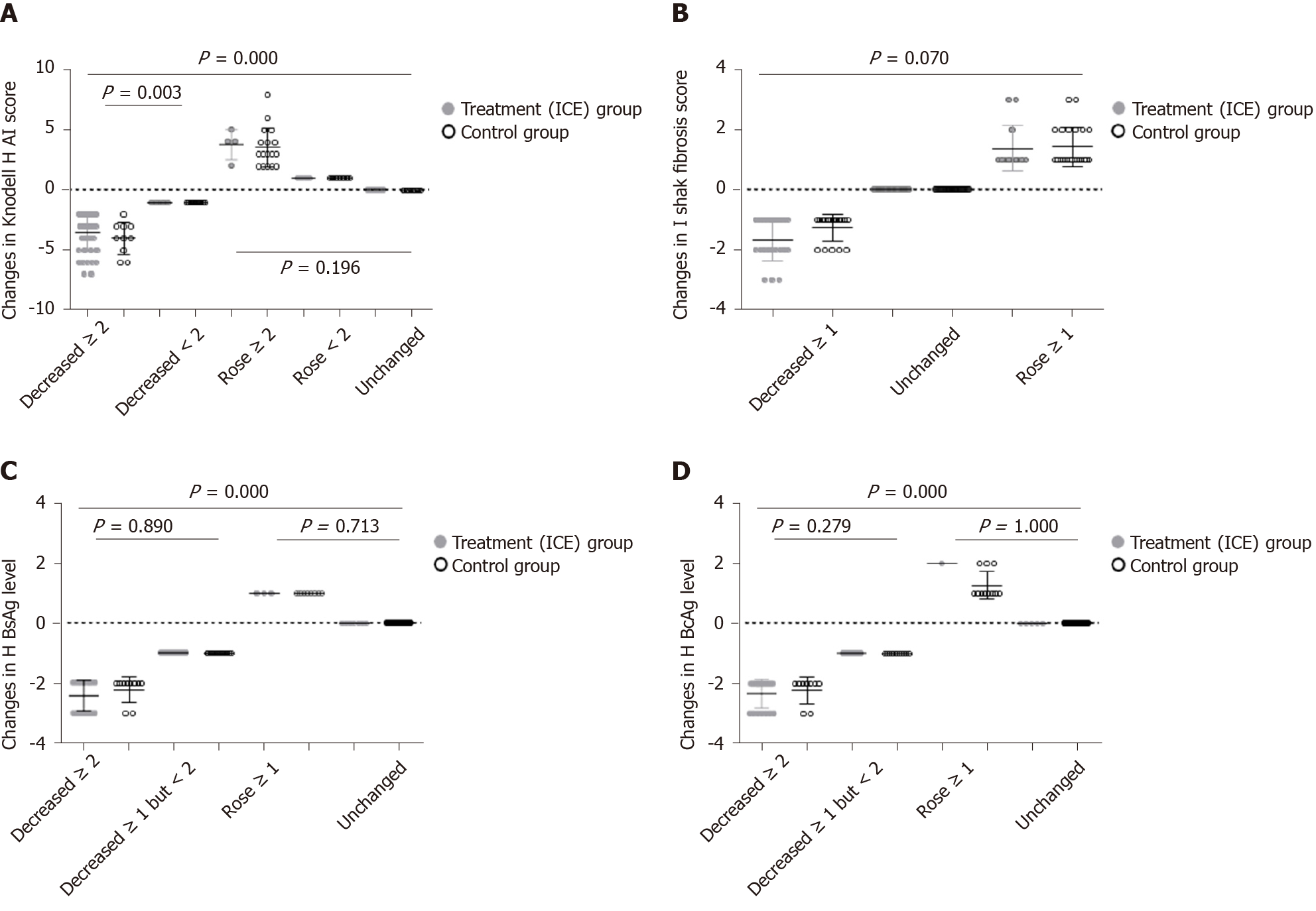
Figure 7 Changes in Knodell histological activity index score, Ishak fibrosis score, liver hepatitis B surface antigen levels and liver hepatitis B core antigen levels at 96 wk after administration in the two groups.
A: Knodell histological activity index score; B: Ishak fibrosis score; C: Liver hepatitis B surface antigen levels; D: Liver hepatitis B core antigen levels. HAI: Histological activity index; HBsAg: Hepatitis B surface antigen; HBcAg: Hepatitis B core antigen.
- Citation: Xing YF, Wei CS, Zhou TR, Huang DP, Zhong WC, Chen B, Jin H, Hu XY, Yang ZY, He Q, Jiang KP, Jiang JM, Hu ZB, Deng X, Yang F, Li FY, Zhao G, Wang LC, Mi YQ, Gong ZJ, Guo P, Wu JH, Shi WQ, Yang HZ, Zhou DQ, Tong GD. Efficacy of a Chinese herbal formula on hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B patients. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(30): 4501-4522
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i30/4501.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i30.4501