Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 7, 2019; 25(37): 5641-5654
Published online Oct 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i37.5641
Published online Oct 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i37.5641
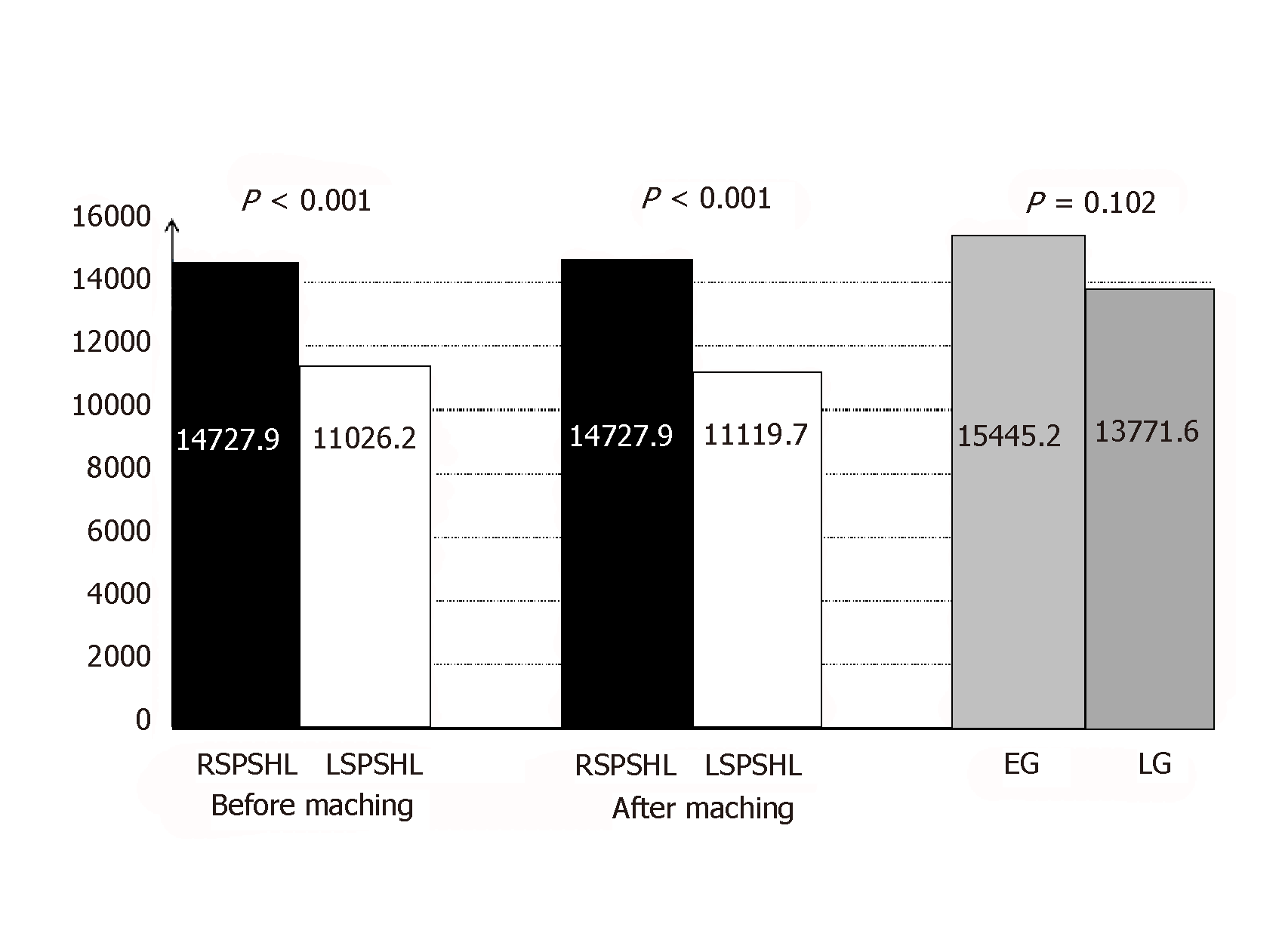
Figure 1 Cost analysis between different groups and subgroups.
RSPSHL: Robotic spleen-preserving splenic hilar lymphadenectomy; LSPSHL: Laparoscopic spleen-preserving splenic hilar lymphadenectomy; EG: Early group; LG: Late group.
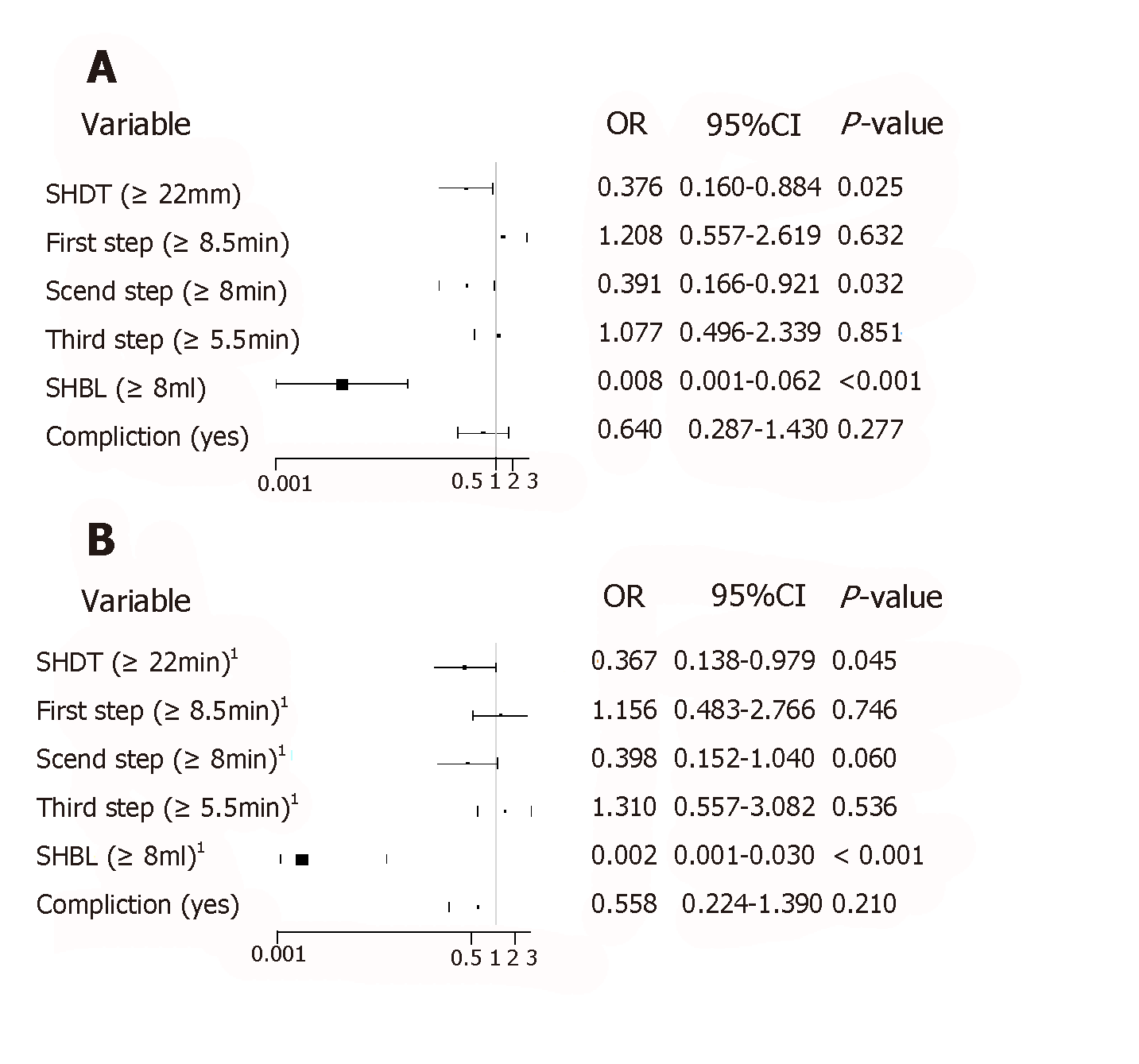
Figure 2 Unadjusted (A) and adjusted (B) regression models of robotic surgery via Huang's three-step maneuver and complications.
1Adjusted for: age, sex, body mass index, American Society of Anesthesiologists class, cT, cN, post-gastric artery, short gastric vessels, splenic upper pole artery, splenic lower pole artery, and the terminal branches of the splenic artery. BMI: Body mass index; ASA: American Society of Anesthesiologists; SGV: Short gastric vessel; PGA: Post-gastric artery; SUPA: Splenic upper pole artery; SLPA: Splenic lower pole artery; SpA: Splenic artery; SHDT: Splenic hilar dissection time; SHBL: Splenic hilar blood loss.
- Citation: Wang JB, Liu ZY, Chen QY, Zhong Q, Xie JW, Lin JX, Lu J, Cao LL, Lin M, Tu RH, Huang ZN, Lin JL, Zheng HL, Que SJ, Zheng CH, Huang CM, Li P. Short-term efficacy of robotic and laparoscopic spleen-preserving splenic hilar lymphadenectomy via Huang's three-step maneuver for advanced upper gastric cancer: Results from a propensity score-matched study. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(37): 5641-5654
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i37/5641.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i37.5641