Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2017; 23(23): 4200-4210
Published online Jun 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i23.4200
Published online Jun 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i23.4200
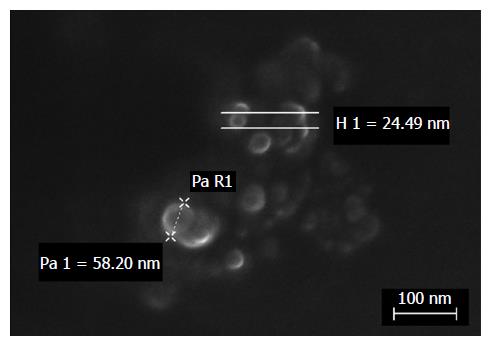
Figure 1 FeSEM micrograph of dexamethasone cholesteryl butyrate-solid lipid nanoparticles.
Electron microscopy analysis showed regular shape and nanosize of particles by height (H) or radius (R) measurements.
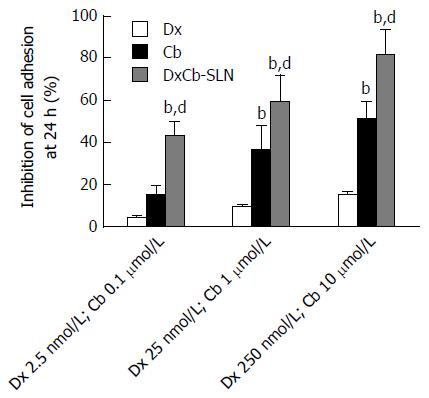
Figure 2 Effect of dexamethasone, cholesteryl butyrate and dexamethasone cholesteryl butyrate-solid lipid nanoparticles on human vascular endothelial cell adhesiveness to Jurkat cells.
Human vascular endothelial cells were pre-activated with IL-1β (0.01 μmol/L) for 1 h and then exposed or not exposed to increasing concentrations of Dx (2.5, 25 and 250 nmol/L), Cb (0.1, 1 and 10 μmol/L) and DxCb-SLN (2.5 nmol/L:0.1 μmol/L, 25 nmol/L:1 μmol/L and 250 nmol/L:10 μmol/L) for 24 h and then incubated with Jurkat for 1 h. bP < 0.01, vs Dx; dP < 0.01, vs Cb. Dx: Dexamethasone; Cb: Cholesteryl butyrate; DxCb-SLN: Dexamethasone cholesteryl butyrate-solid lipid nanoparticles.
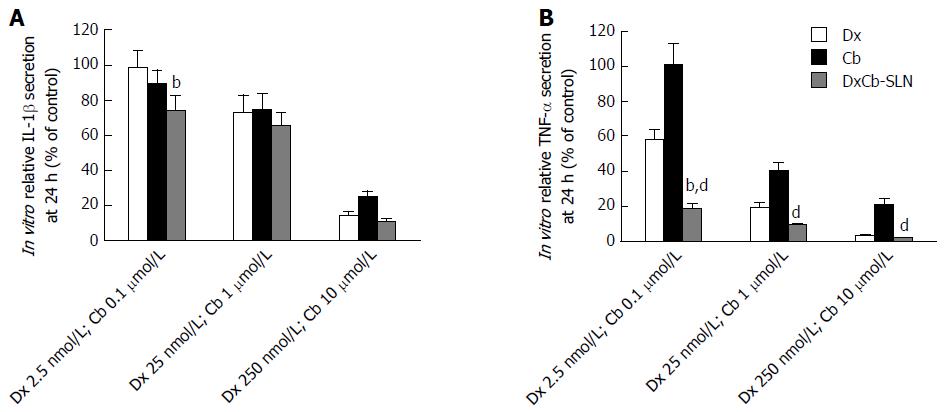
Figure 3 In vitro effect of dexamethasone, cholesteryl butyrate and dexamethasone cholesteryl butyrate-solid lipid nanoparticles on interleukin-1β and tumor necrosis factor-α secretion.
Cells were treated with increasing concentrations of Dx (2.5, 25 and 250 nmol/L), Cb (0.1, 1 and 10 μmol/L) and DxCb-SLN (2.5 nmol/L:0.1 μmol/L, 25 nmol/L:1 μmol/L and 250 nmol/L:10 μmol/L) for 24 h. IL-1β (A) and TNF-α (B) secretion in culture supernatant of PBMCs stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS; 1 μg/mL for 24 h) were analyzed by ELISA. bP < 0.01, vs Dx; dP < 0.01, vs Cb. Dx: Dexamethasone; Cb: Cholesteryl butyrate; DxCb-SLN: Dexamethasone cholesteryl butyrate-solid lipid nanoparticles; IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor.
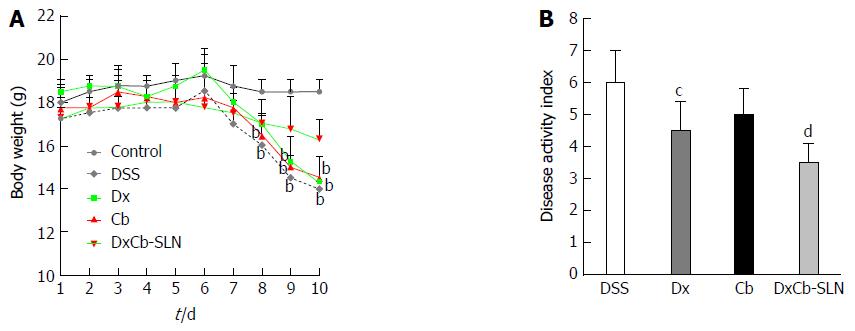
Figure 4 In vivo effect of dexamethasone, cholesteryl butyrate and dexamethasone cholesteryl butyrate-solid lipid nanoparticles on bodyweight and disease activity index.
Animals received no treatment (control), DSS alone (DSS), or a combination of DSS and Dx (Dx, 0.0001 mg/g bw for 3 d), DSS and Cb (Cb, 0.004 mg/g bw for 3 d) and DSS and DxCb-SLN (DxCb-SLN, 0.0001 mg/g bw:0.004 mg/g bw for 3 d). After 7 d, DSS was replaced with a water cycle (ad libitum) for another 7 d. Body weight of the mice was recorded daily (A) and the disease activity rate at day 9 (B). bP < 0.01, vs control; cP < 0.05; dP < 0.01, vs DSS. Dx: Dexamethasone; Cb: Cholesteryl butyrate; DxCb-SLN: Dexamethasone cholesteryl butyrate-solid lipid nanoparticles; DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium.
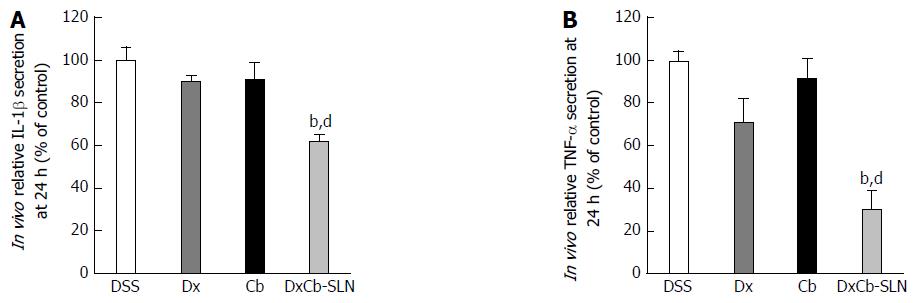
Figure 5 In vivo effect of dexamethasone, cholesteryl butyrate and dexamethasone cholesteryl butyrate-solid lipid nanoparticles on interleukin-1β and tumor necrosis factor-α secretion.
Animals were treated with DSS alone (DSS), or a combination of DSS and Dx (Dx, 0.0001 mg/g bw for 3 d), DSS and Cb (Cb, 0.004 mg/g bw for 3 d) and DSS and DxCb-SLN (DxCb-SLN, 0.0001 mg/g bw:0.004 mg/g bw for 3 d). IL-1β and TNF-α secretion in mice plasma were analyzed by ELISA at day 9, 24 h after drug treatment. bP < 0.01, vs Dx; dP < 0.01, vs Cb. Dx: Dexamethasone; Cb: Cholesteryl butyrate; DxCb-SLN: Dexamethasone cholesteryl butyrate-solid lipid nanoparticles; DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium; IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor.
- Citation: Dianzani C, Foglietta F, Ferrara B, Rosa AC, Muntoni E, Gasco P, Della Pepa C, Canaparo R, Serpe L. Solid lipid nanoparticles delivering anti-inflammatory drugs to treat inflammatory bowel disease: Effects in an in vivo model. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(23): 4200-4210
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i23/4200.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i23.4200