Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2016; 22(39): 8735-8749
Published online Oct 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i39.8735
Published online Oct 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i39.8735
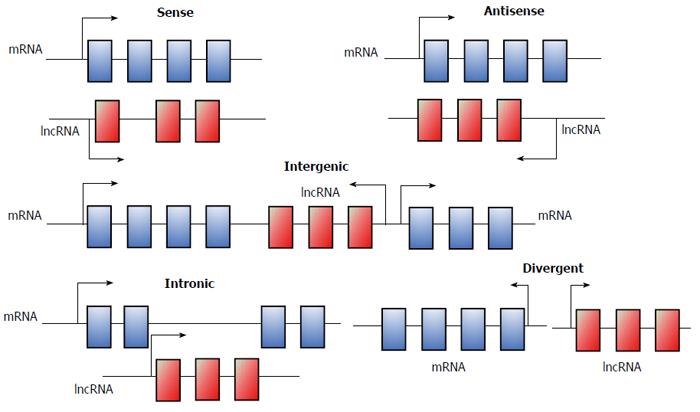
Figure 1 Five brief categories of long noncoding RNAs based on the genome position.
lncRNAs: Long noncoding RNAs.
Figure 2 Mechanisms of long noncoding RNAs according to the subcellular localization.
lncRNAs in nucleus frequently interact with protein complexes (such as PRC2) to modify chromatin structures. LncRNAs can also recruit transcription factors to promote or repress gene transcription, through regulating SR proteins, or form RNA-RNA duplexes with pre-mRNAs. Some lncRNAs (such as H19) are spliced into pri-miRNAs, which contributed to miRNA processing. In cytoplasm, lncRNAs may form specific structures with mRNA and interact with some active elements or repressive elements to modulate mRNA translation. By forming RNA-RNA complementary sites with mRNA or microRNA, lncRNAs can promote or inhibit mRNA stability and serve as “sponges” for miRNAs. lncRNAs: Long noncoding RNAs; PRC2: Polycomb repressive complex2.
Figure 3 Regulating function of metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 in gastrointestinal cancer.
CCL5 secreted by tumor-associated dendritic cells (TADCs) can promote MALAT1 expression. MALAT1 activates the ERK/MAPK pathway and Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Snail and AKAP-9 are downstream targets of MALAT1. miR-101 and miR-217 can regulate MALAT1 in 3’UTR region. MALAT1 can also bind to SFPQ/PTBP2 complex and promote the release of PTBP2. MALAT1: Metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1.
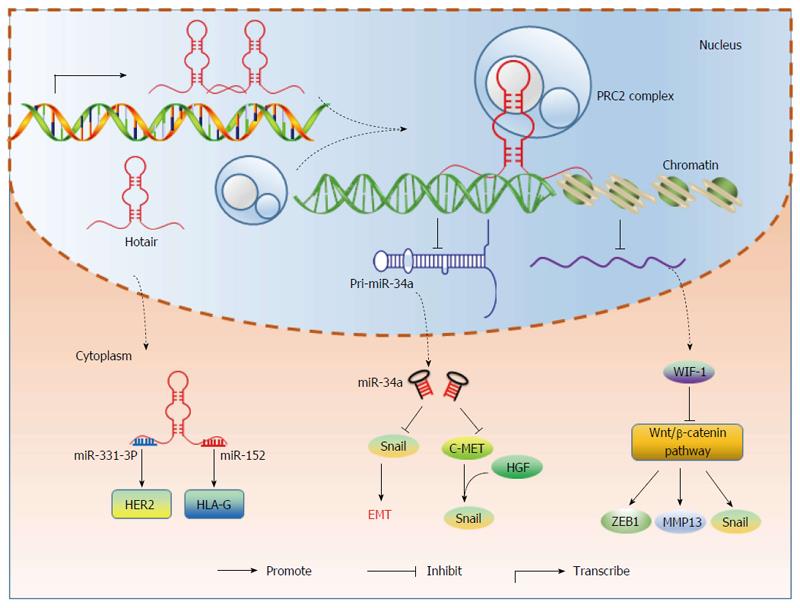
Figure 4 Regulating function of HOTAIR in gastrointestinal cancer.
In nucleus, HOTAIR recruits PRC2 complex and represses pri-miR-34a transcription epigenetically. By inducing histone H3K27 methylation in WIF-1’s promoter region, HOTAIR decreases WIF-1 expression. In cytoplasm, HOTAIR serves as “sponges” for miR-331-3p and miR-152, leading to the increase of target genes HER2 and HLA-G. PRC2: Polycomb repressive complex2.
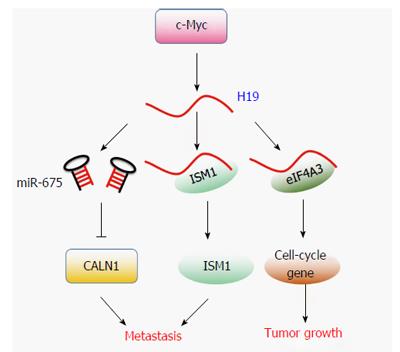
Figure 5 Regulating function of H19 in gastrointestinal cancer.
H19 is transcribed by transcription factor c-Myc. H19 can be spliced into pre-miRNA of miR-675, and suppresses miR-675 target gene CALN1. H19 also binds with its binding protein ISM1 or Eif4A3 and promotes metastasis or growth.
- Citation: Zhang FF, Luo YH, Wang H, Zhao L. Metastasis-associated long noncoding RNAs in gastrointestinal cancer: Implications for novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(39): 8735-8749
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i39/8735.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i39.8735