Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2014; 20(10): 2664-2672
Published online Mar 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i10.2664
Published online Mar 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i10.2664
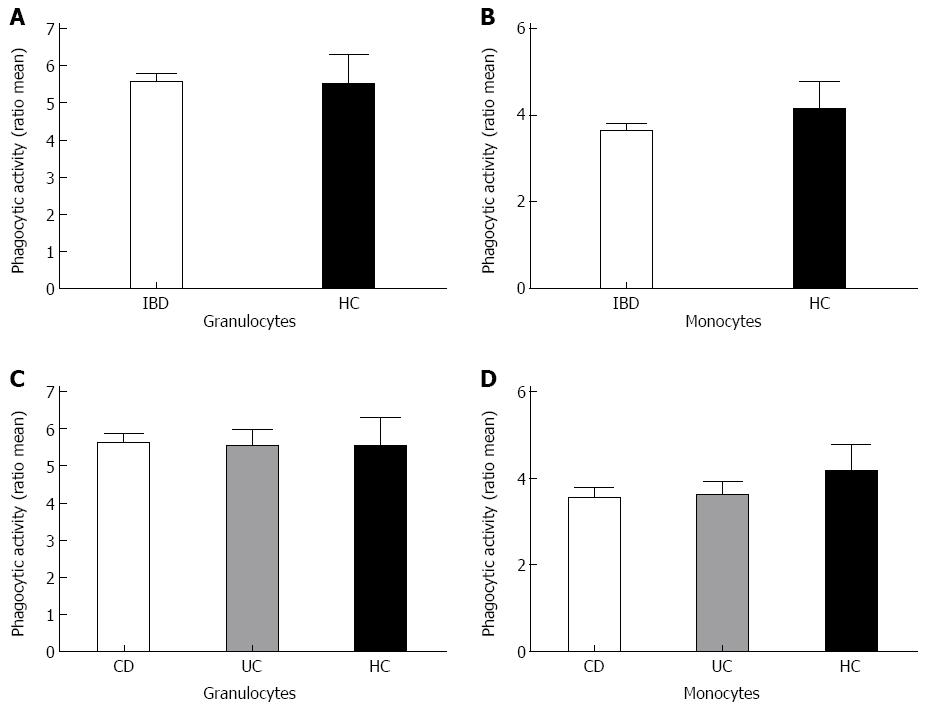
Figure 1 Phagocytic activity of the disease groups compared to healthy controls.
Bars represent ratio of the mean phagocytic activity. Total inflammatory bowel disease patients (IBD) patients (A, B for granulocytes and monocytes respectively) were analyzed as well as for separate Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC) patients compared to healthy controls (C, D). HC: Healthy controls.
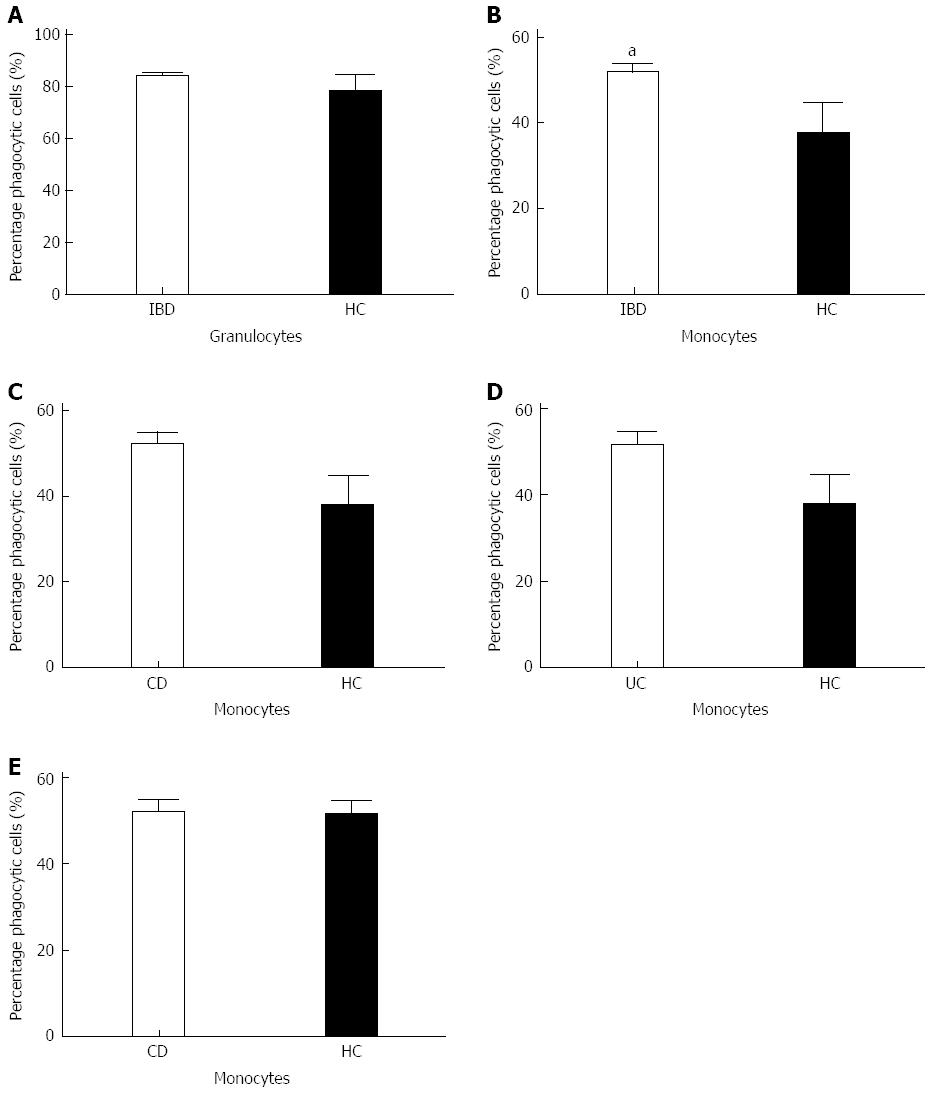
Figure 2 Percentage of phagocytic cells in inflammatory bowel disease patients patients and healthy controls.
A: Percentages of active granulocytes are comparable between both groups; B: Significantly higher amount of active phagocytic monocytes was found in the inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) patient group compared to healthy controls (P = 0.0408), aP < 0.05 vs HC group; C: Crohn’s disease (CD) patients show a significantly higher percentage of active phagocytic monocytes compared to healthy controls; D, E: This was not seen when compared to ulcerative colitis (UC) patients. Bars represent means.
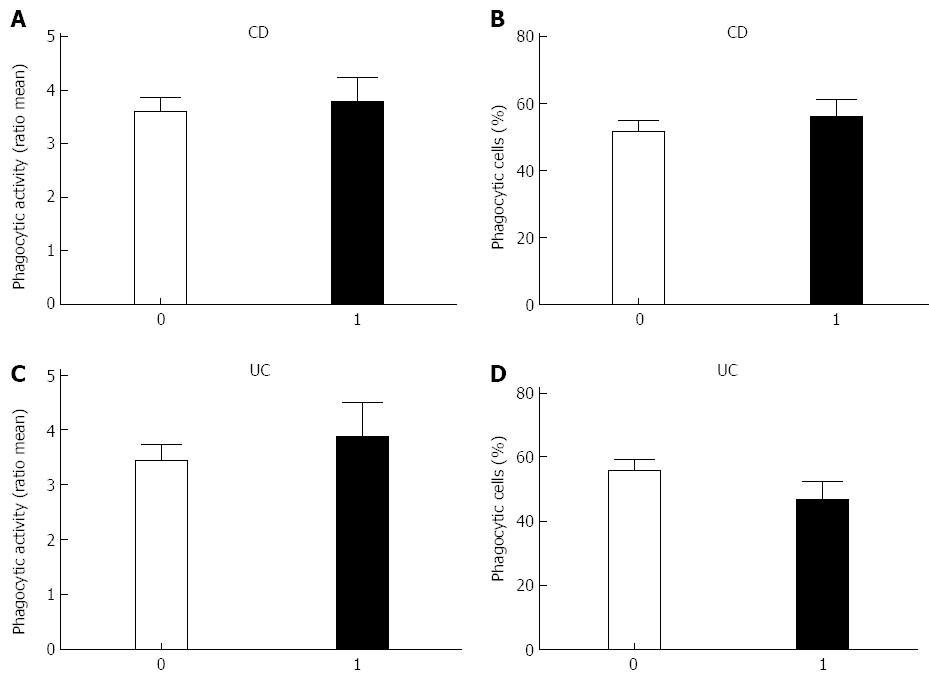
Figure 3 Phagocytic activity and percentage of phagocytic cells and the correlation with disease activity in Crohn’s disease patients and ulcerative colitis patients.
A, B: Crohn’s disease (CD); C, D: Ulcerative colitis (UC). 0: No disease activity; 1: Disease activity.
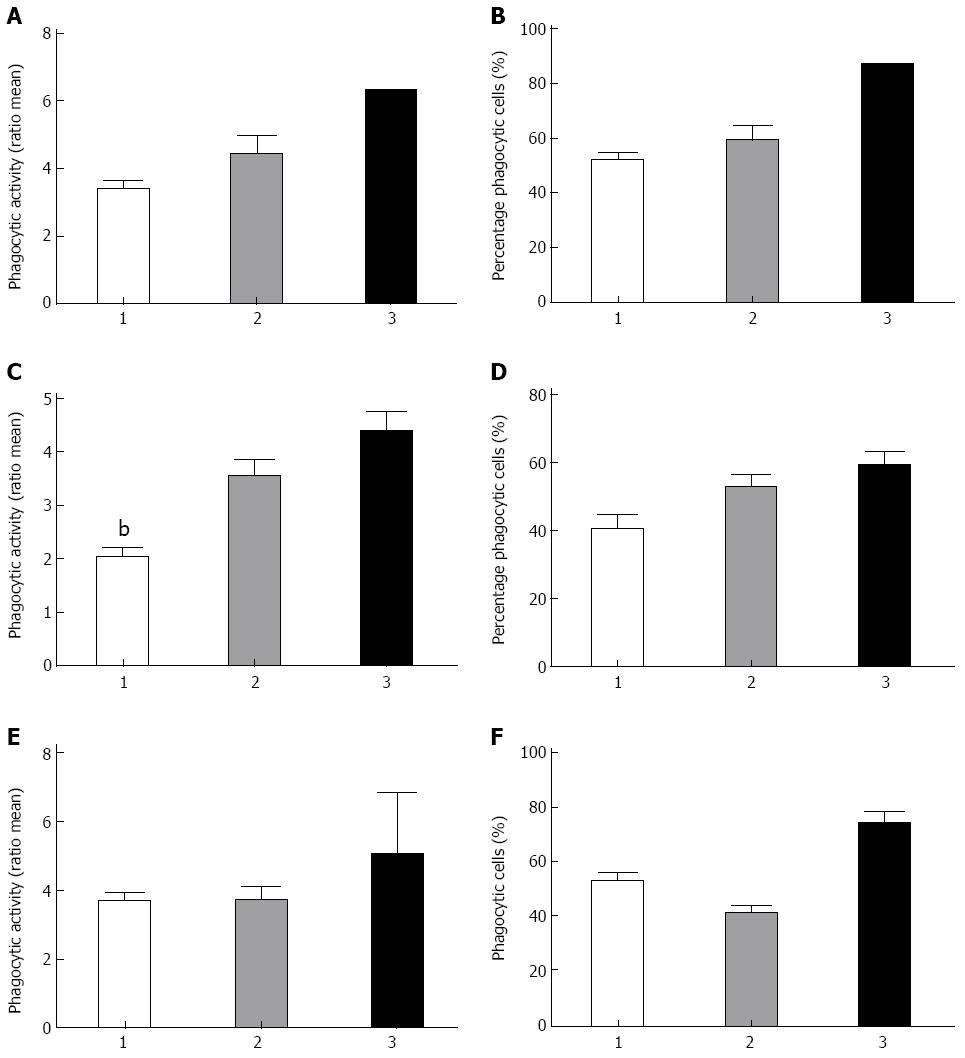
Figure 4 Phagocytosis and variants in Crohn’s disease associated genes autophagy related like 1, immunity-related guanosine triphosphatase gene and nucleotide-binding ligomerization domain-containing protein 2.
A, B: Genotypes in immunity-related guanosine triphosphatase variant and association with either phagocytic activity or the percentage of active monocytes, respectively; C, D: Genotypes of the autophagy related like 1 variant associated with enhanced phagocytic activity (P = 0.009) and percentage of active monocytes respectively. bP < 0.01 vs genetype 3; E, F: The genotype of the variant 3020 C-ins of nucleotide-binding ligomerization domain-containing protein 2 and phagocytic activity as well as the percentage of active monocytes (P = 0.05) respectively. Genotypes 1: Wild type; Genotypes 2: Heterozygous variant; Genotypes 3: Homozygous variant.
-
Citation: Wolfkamp SC, Verseyden C, Vogels EW, Meisner S, Boonstra K, Peters CP, Stokkers PC, te Velde AA.
ATG16L1 andNOD2 polymorphisms enhance phagocytosis in monocytes of Crohn’s disease patients. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(10): 2664-2672 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i10/2664.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i10.2664