Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2013; 19(30): 4850-4860
Published online Aug 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i30.4850
Published online Aug 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i30.4850
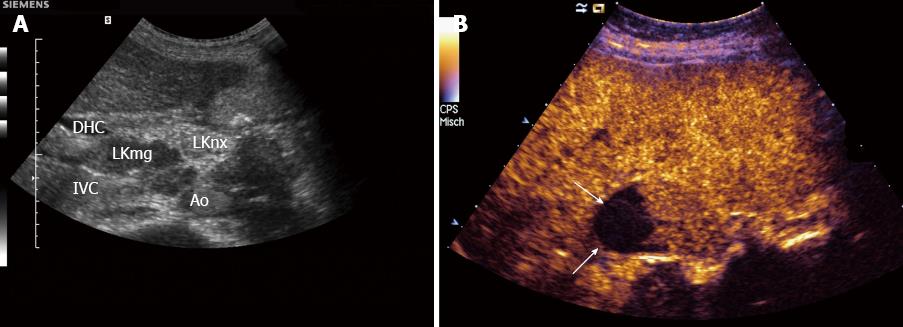
Figure 1 Lymph node infiltration, carcinoma.
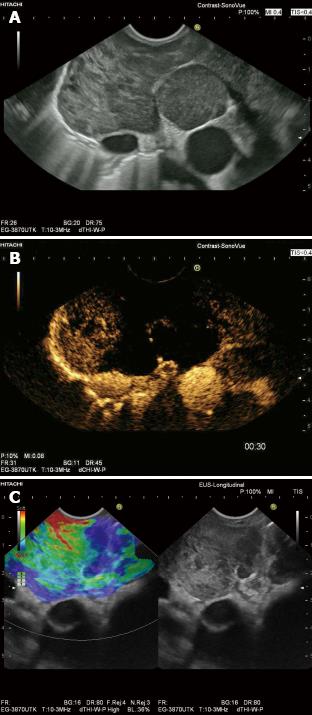
A: With lymph node (LN) specific contrast agents malignant infiltration can be delineated (LKmg) as focal hypoenhancement in the upper part of this perihepatic LN. The lower part (LKnx) shows normal (physiological) enhancement; B: With SonoVue®. Necrotic (non-enhancing, arrows) areas can be detected within this perihepatic lymph node. Necrotic areas are typically for carcinoma infiltration and tuberculosis. IVC: Inferior vena cava; Ao: Aorta; DHC: Common bile duct.
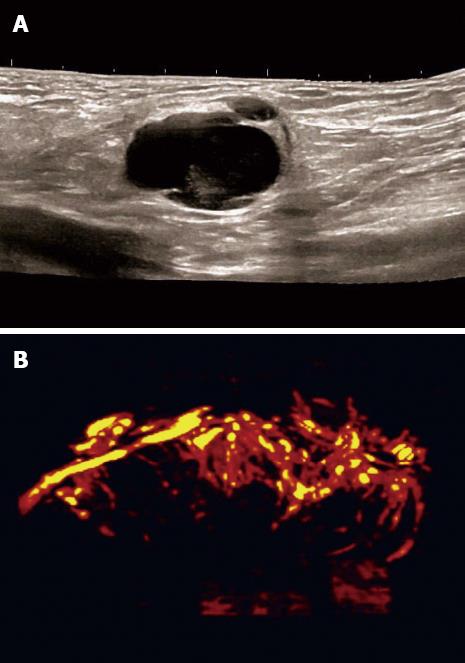
Figure 2 Carcinoma infiltration.
Typically vessel destruction with chaotic vessels in the lymph node can be observed. B-mode (A) and 3D angiographic mode (B).
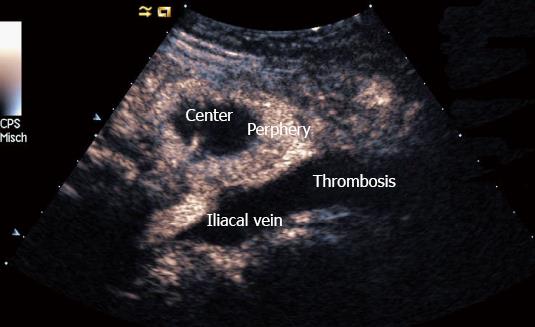
Figure 3 Prostate carcinoma infiltration of the pelvis.
Typically vessel destruction with interruption of vessel architecture can be observed in patients with carcinoma. The center of the lymph node is almost non-enhancing except one visible vessel whereas the periphery shows hyperenhancement. Thrombosis of the iliac vein is indicated as well.
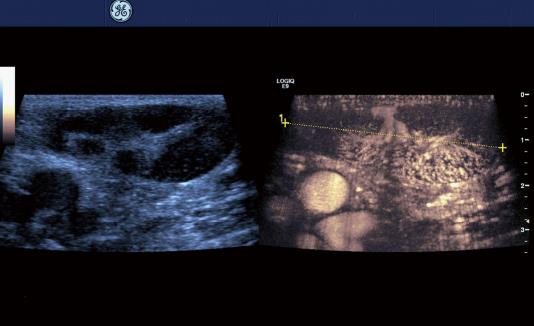
Figure 4 Lymph node infiltration (50 mm), non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
Typically the hilum predominant vessel architecture is preserved (between markers).
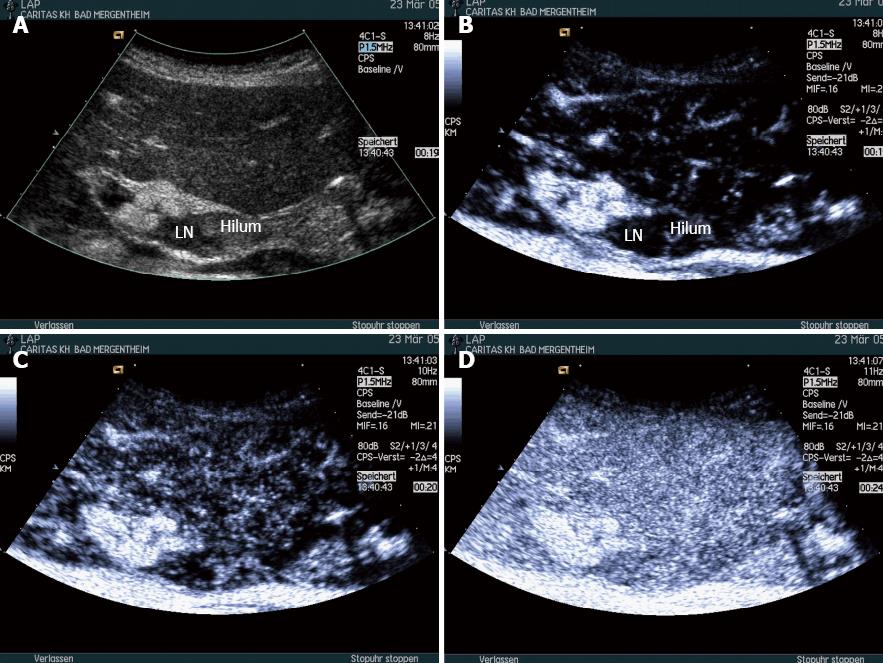
Figure 5 Inflammatory perihepatic lymph node dorsal in the hepatoduodenal ligament.
Inflammation most often shows no changes of the symmetric lymph node vascularity and homogenous contrast enhancement (A-D). The hilum is indicated. LN: Lymph node.
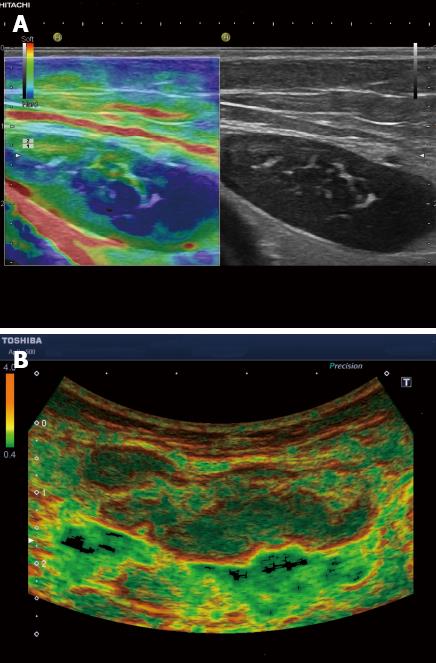
Figure 6 Colorectal carcinoma with presacral circumscribed lymph node metastasis proven by colonic endoscopic ultrasound using Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology.
Sonoelastography reliability test evaluation reveals typically harder (blue) area in the lymph node.
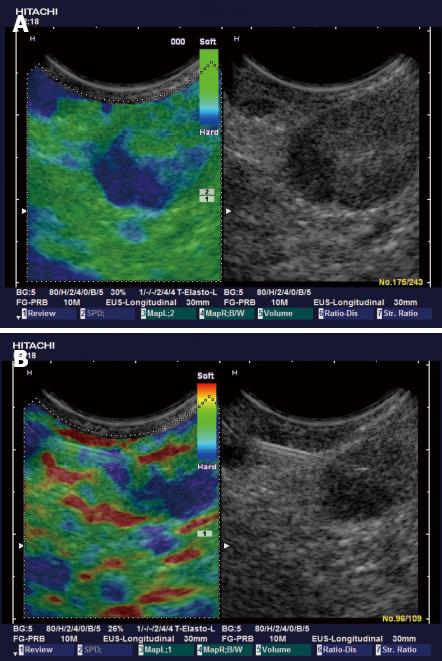
Figure 7 Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma involving the inguinal region.
A: Sonoelastography reliability test evaluation reveals typically asymmetric and circumscribed infiltrated harder (blue) lymph node tissue in low grade follicular cell lymphoma; B: Elastography (acoustic structured quantification) reveals mainly homogenous diffuse infiltration in high grade follicular cell lymphoma.
Figure 8 Endosonography.
Enlarged subcarinal lymph nodes in Non Hodgkin Lymphoma (A: B-Mode). Contrast enhanced endoscopic ultrasound demonstrates extensive avascular (necrotic) areas (B) and real time endoscopic indicates hard (blue), infiltrated areas (C), thus targeting endoscopic ultrasound-guided biopsy.
- Citation: Cui XW, Jenssen C, Saftoiu A, Ignee A, Dietrich CF. New ultrasound techniques for lymph node evaluation. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(30): 4850-4860
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i30/4850.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i30.4850