Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2012; 18(10): 1067-1076
Published online Mar 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i10.1067
Published online Mar 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i10.1067
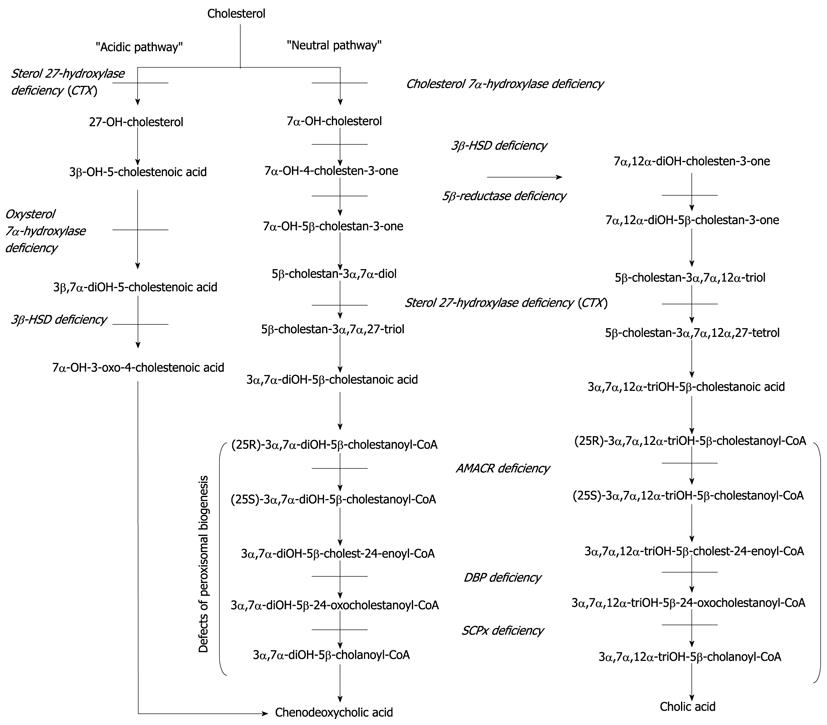
Figure 1 The metabolic pathway of bile acid biosynthesis.
The classical “neutral pathway” with chenodeoxycholic acid and cholic acid as end products is the main pathway in adults. In children, the alternative “acidic pathway” with chenodeoxycholic acid as major product is more active. The end products are exported as glycine or taurine conjugates into the bile canaliculi. Known metabolic blocks are displayed as bars and the specific defects in italic script. CTX: Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis.
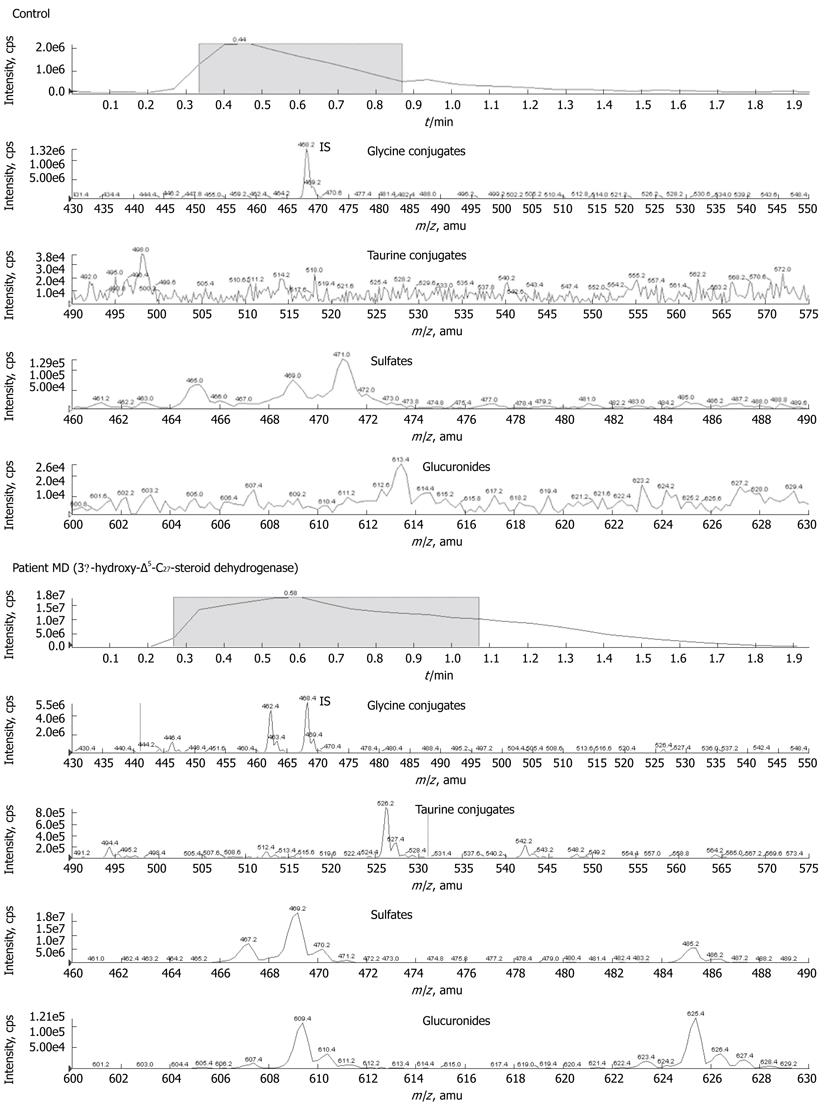
Figure 2 Precursor ion spectra of urinary bile acid metabolites from patient MD with 3β-hydroxy-Δ5-C27-steroid dehydrogenase deficiency and control.
The strongest signals were identified as sulphate conjugates of di- and trihydroxy-5-cholenoic acid scanning with m/z 469 and 485. Glycine conjugates of di- and trihydroxy-5-cholenoic acid (m/z 526 and 542) were less pronounced, but also increased.
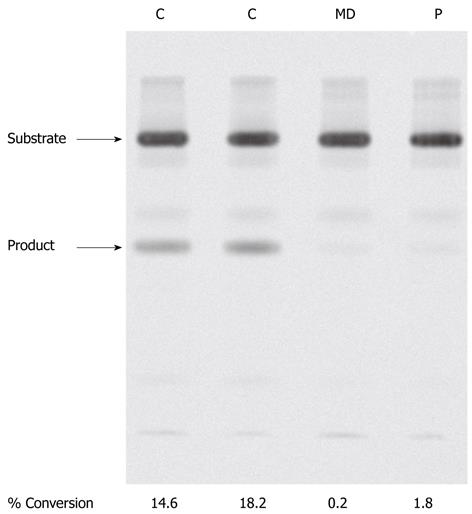
Figure 3 3β-hydroxy-Δ5-C27-steroid dehydrogenase activity in patient fibroblasts.
In control cells (C) two sterols were observed after thin layer chromatography. These compounds were identified by gas chromatography mass spectrometry as the substrate, 7α-hydroxycholesterol and product, 7α-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one, of 3β-hydroxy-Δ5-C27-steroid dehydrogenase. In fibroblasts of patient MD and another patient with known 3β-hydroxy-Δ5-C27-steroid dehydrogenase deficiency (P), little or no 7α-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one was formed.
- Citation: Haas D, Gan-Schreier H, Langhans CD, Rohrer T, Engelmann G, Heverin M, Russell DW, Clayton PT, Hoffmann GF, Okun JG. Differential diagnosis in patients with suspected bile acid synthesis defects. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(10): 1067-1076
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i10/1067.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i10.1067