Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 7, 2010; 16(37): 4677-4684
Published online Oct 7, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i37.4677
Published online Oct 7, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i37.4677
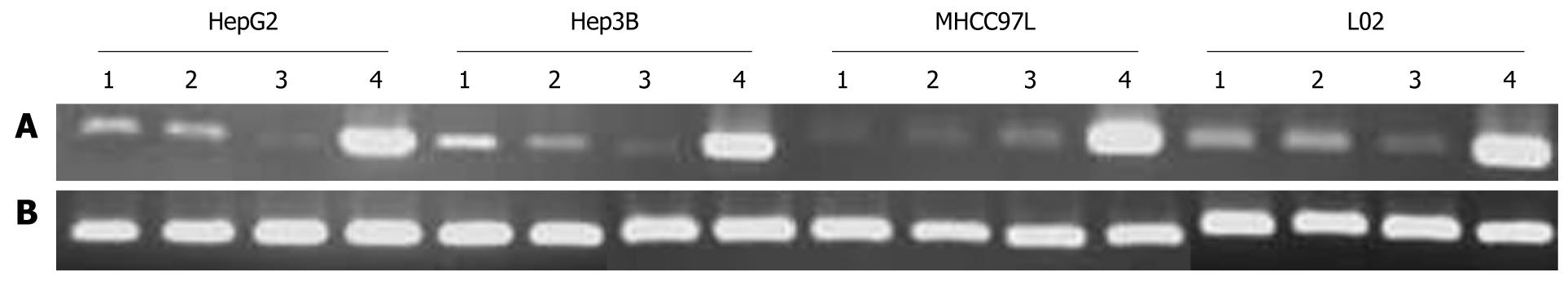
Figure 1 Expression of adenovirus-mediated melanoma differentiation-associated-7/interleukin-24 mRNA in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines of HepG2, Hep3B and MHCC97L and human normal liver cell line L02.
Cells were infected with 10 multiplicity of infection of Ad.IL-24, SG600-EGFP, SG600-IL24,harvested at 24 h, treated as described in “Materials and Methods”. A: Lanes 1, 2, 3, 4: Ad.IL-24 group, SG600-EGFP group, control group and SG600-IL24 group; B: β-actin corresponsively.
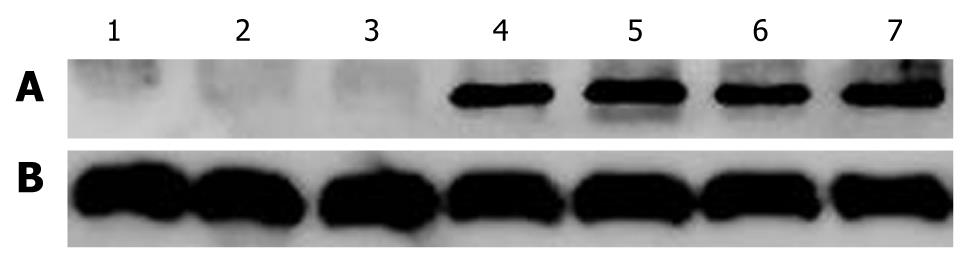
Figure 2 Expression of melanoma differentiation-associated-7/interleukin-24 after infection with SG600-IL24 protein in hepatocellular carcinoma cells and normal liver cells.
Cells infected with 10 multiplicity of infection of Ad.IL-24, SG600-EGFP and SG600-IL24 were collected 48 h after infection as described in “Materials and Methods”. A: Lane 1: Control group; Lane 2: Ad.IL-24 group; Lane 3: SG600-EGFP group; Lanes 4, 5, 6, 7: HepG2, Hep3B, MHCC97L and L02 SG600-IL24 groups; B: β-actin corresponsively.
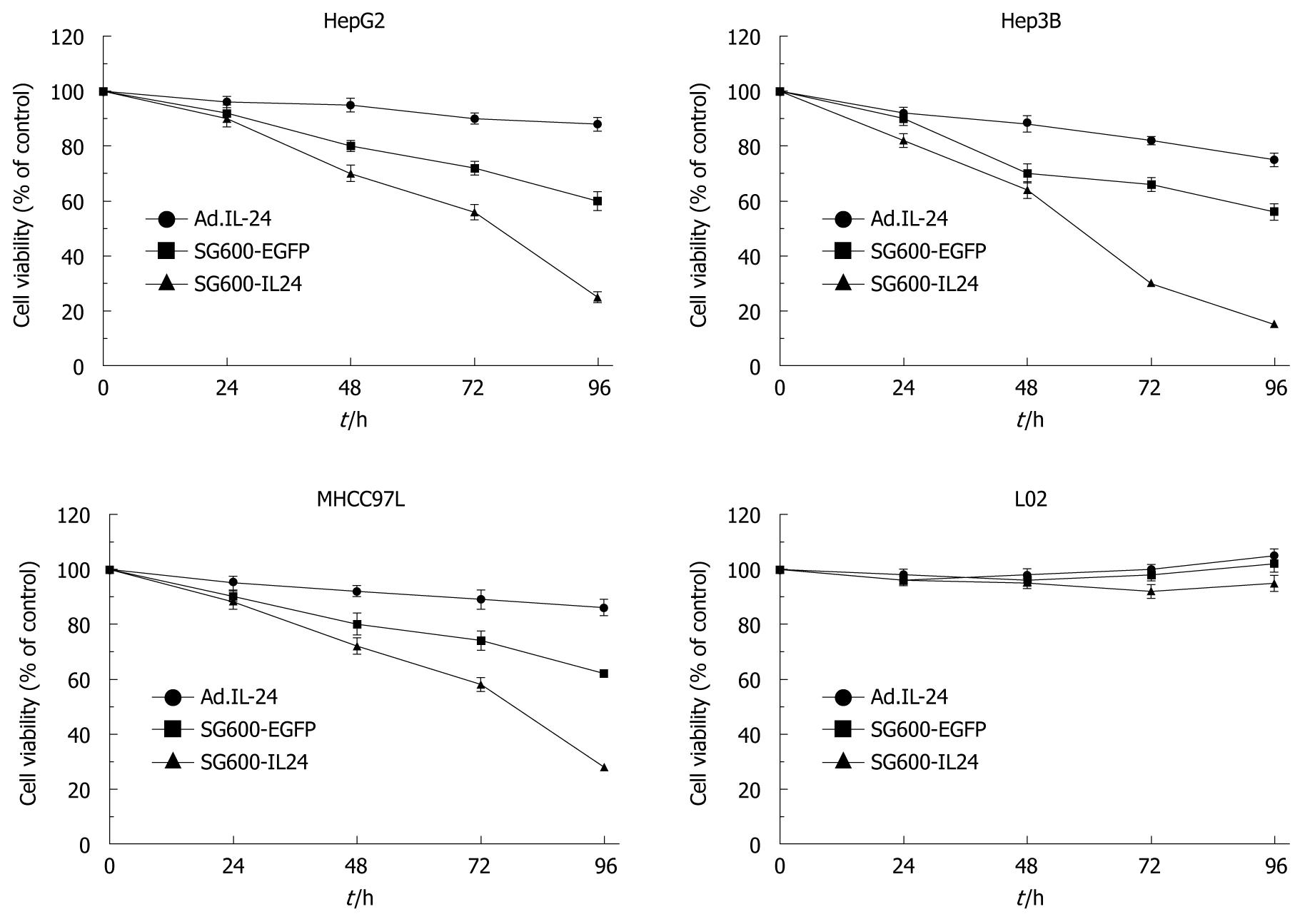
Figure 3 Cell viability of different hepatocellular carcinoma cells and normal liver cells infected with oncolytic adenoviruses SG600-IL24 and replicant replication-deficient adenovirus Ad.
IL-24 measured by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay at 24, 48, 72 and 96 h after infection. Results are presented as means ± SD (n = 5).
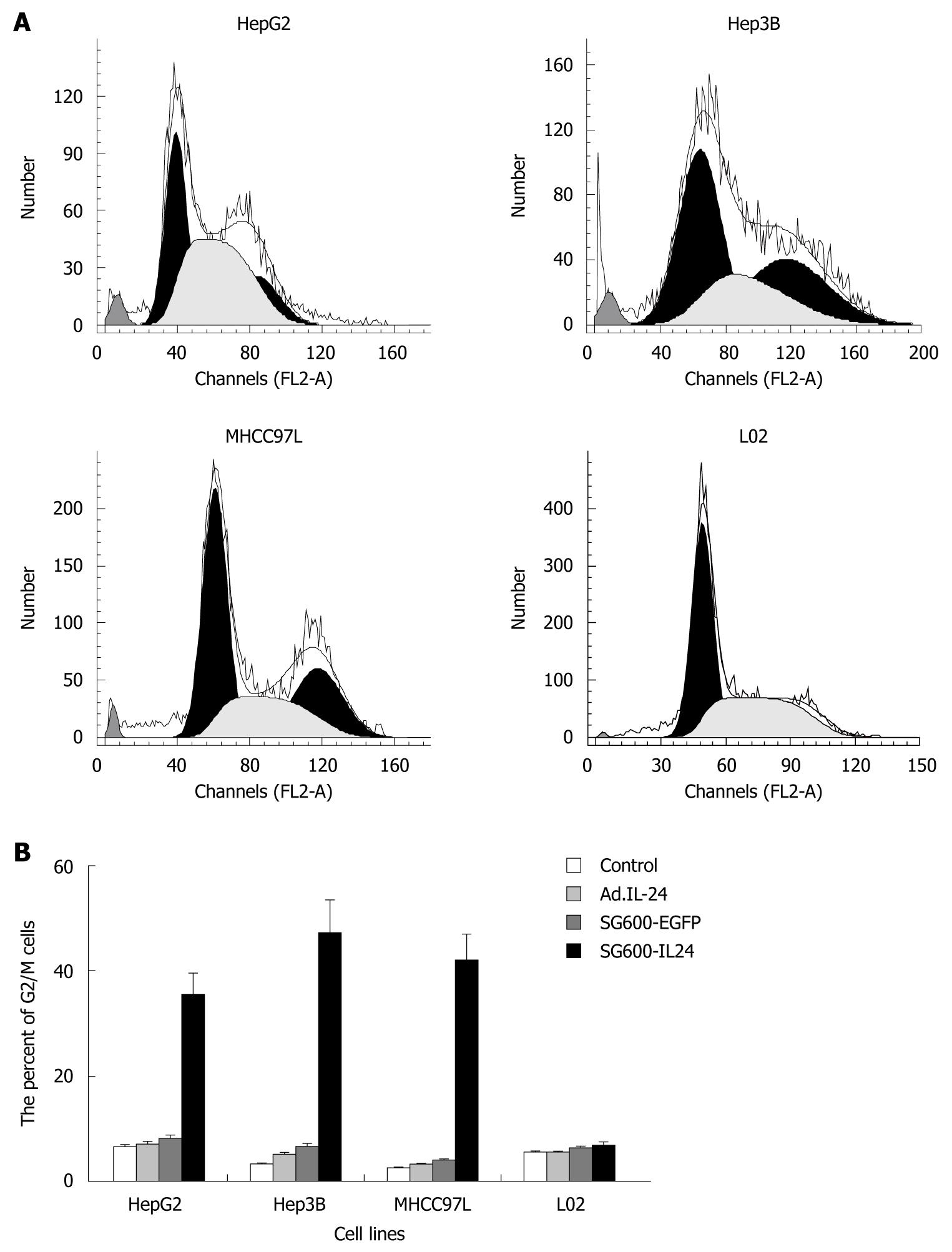
Figure 4 Flow cytometry (A) and histography (B) showing SG600-IL24 induced G2/M arrest in hepatocellular carcinoma cells after SG600-IL24 infection.
- Citation: Xue XB, Xiao CW, Zhang H, Lu AG, Gao W, Zhou ZQ, Guo XL, Zhong MA, Yang Y, Wang CJ. Oncolytic adenovirus SG600-IL24 selectively kills hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(37): 4677-4684
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i37/4677.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i37.4677