Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2006; 12(40): 6453-6457
Published online Oct 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i40.6453
Published online Oct 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i40.6453
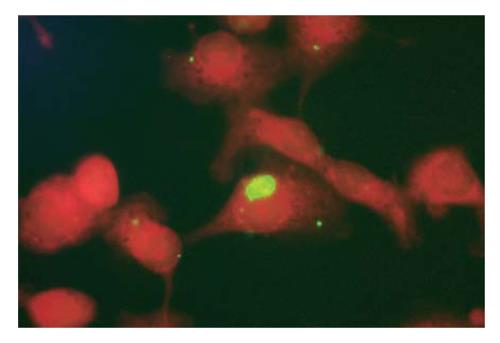
Figure 1 IFA for the detection of C.
pneumoniae antigens in separated Kupffer cells. 1000 x. Kupffer cells separated from intraperitoneally infected mice sacrificed 7 d after infection were tested by immunofluorescence assay (IFA) with specific fluorescein-conjugated monoclonal antibodies. A positive Kupffer cell is clearly evident for the presence of an apple-green intracytoplasmic bacterial inclusion. The inclusion represents an intracytoplasmic bacterial microcolony.
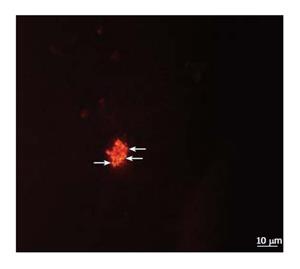
Figure 2 FISH for C.
pneumoniae 16S rRNA in separated Kupffer cells. In situ hybridization was performed on Kupffer cells separated from intraperitoneally infected mice, sacrificed 7 d after infection. An infected Kupffer cell is evidenced with Cpn-0974 specific probe: the granular inclusion stained red.
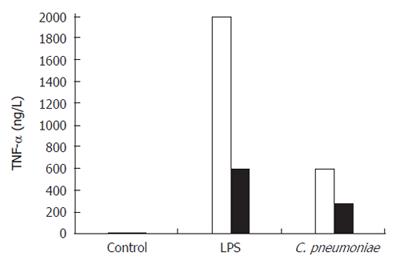
Figure 3 TNF-α release by Kupffer cells following in vitro exposure to alive C.
pneumoniae. Kupffer cells were stimulated for 6 h with alive C. pneumoniae. Control LPS was used at 10 mg/L. Stimulation was performed with (black) or without (white) polymyxin B at concentration of 10 mg/L.
-
Citation: Marangoni A, Donati M, Cavrini F, Aldini R, Accardo S, Sambri V, Montagnani M, Cevenini R.
Chlamydia pneumoniae replicates in Kupffer cells in mouse model of liver infection. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(40): 6453-6457 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i40/6453.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i40.6453