Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2006; 12(17): 2737-2741
Published online May 7, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i17.2737
Published online May 7, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i17.2737
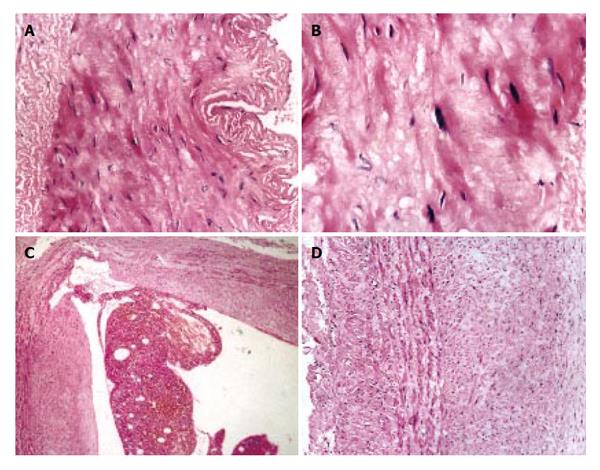
Figure 1 Changes of splenic arteries (A, B) and splenic veins (C, D) in patients with portal hypertension.
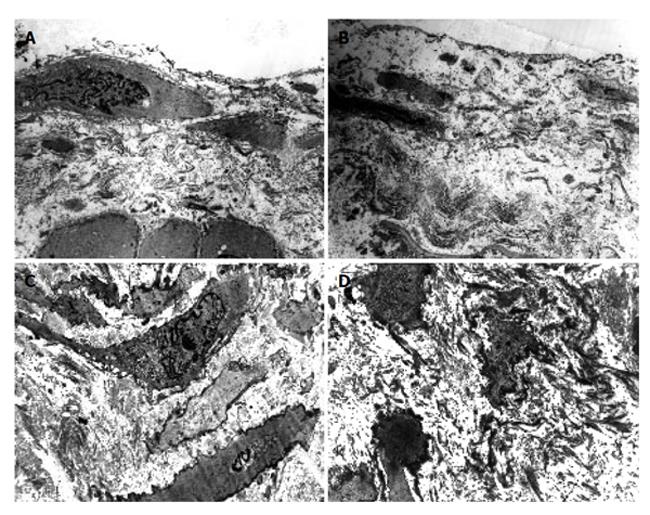
Figure 2 Ultrastructure of splenic artery (A, B) and splenic vein (C, D) in patients with portal hypertension.
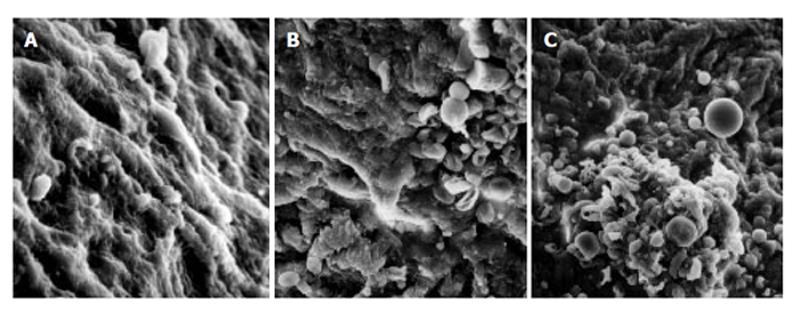
Figure 3 Observation of splenic vein in patients with traumatic splenic rupture without liver cirrhosis (A), in patients with portal hypertension (B), and in patients with portal hypertension (C) under scanning electron microscope.
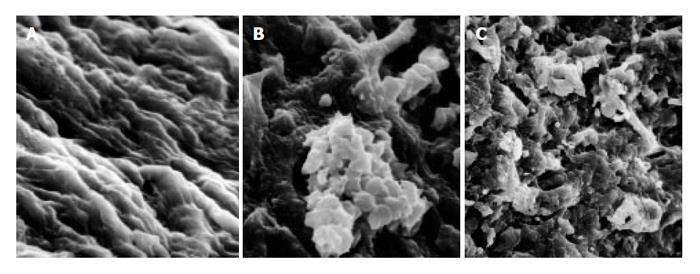
Figure 4 Observation of splenic artery in patients with traumatic splenic rupture without liver cirrhosis (A), in patients with portal hypertension (B), and in patients with portal hypertension (C) under scanning electron microscope.
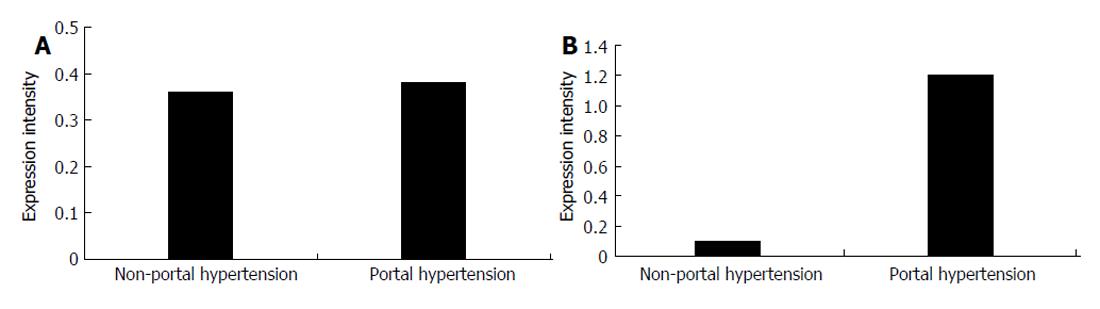
Figure 5 Comparison of the expression intensity of type I (A) and type III (B) procollagen mRNA in splenic vein wall of patients with and without portal hypertension.
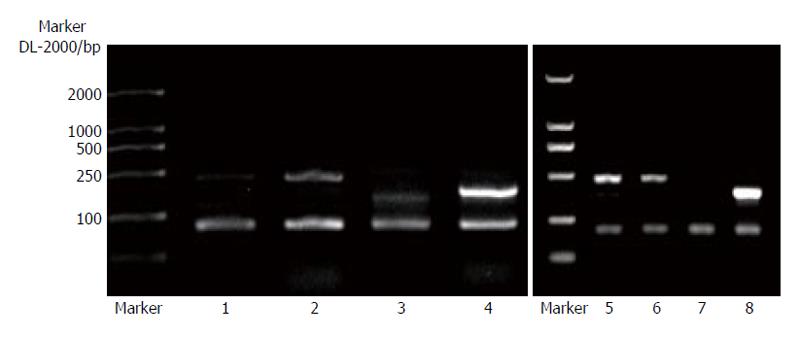
Figure 6 Expression of type III procollagen mRNA of splenic vein wall in patients with portal hypertension.
Bands 1, 3, 5 and 7: control samples from patients without portal hypertension; Bands 2, 4, 6 and 8: samples from patients with portal hypertension.
- Citation: Li T, Ni JY, Qi YW, Li HY, Zhang T, Yang Z. Splenic vasculopathy in portal hypertension patients. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(17): 2737-2741
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i17/2737.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i17.2737