Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 15, 2004; 10(24): 3683-3687
Published online Dec 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i24.3683
Published online Dec 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i24.3683
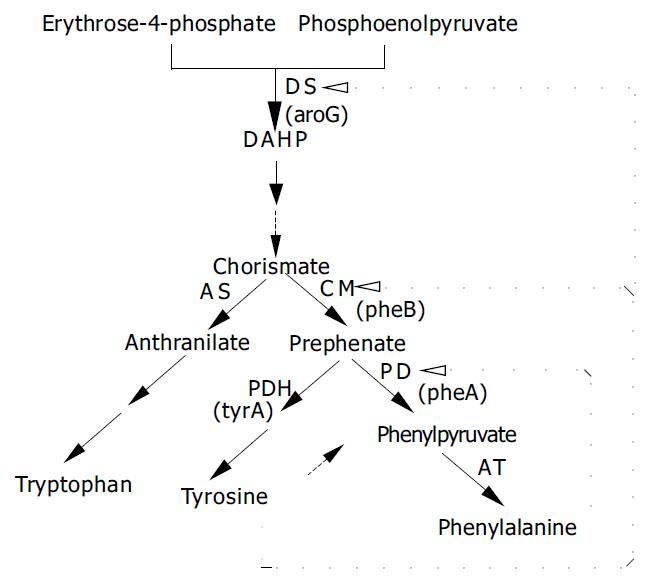
Figure 1 Pathway and primary regulations of phenylalanine biosynthesis in C.
glutamicum←---indicates feedback inhibition, ---→indicates activation.
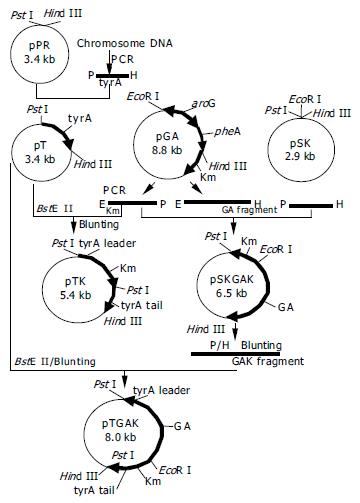
Figure 2 Construction of recombinant plasmids.
E: EcoRI; P: PstI; H: Hind III; GA: PBF-aroG-pheA-T fragment; GAK: PBF-aroG-pheA-T-Km fragment.
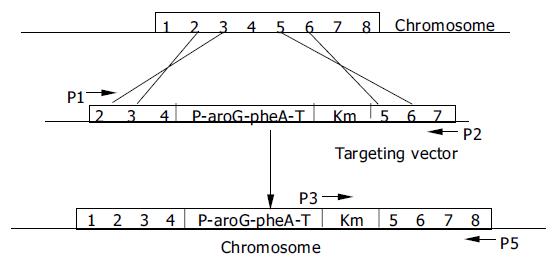
Figure 3 Insertion of PBF-aroG-pheA-T-Km fragment of pTGAK into chromosome tyrA locus of C.
glutamicum by double-ex-change homologous recombination and detection of ligated DNA fragment Km-tyrA tail on chromosome by PCR ampli-fication with P3 and P5.
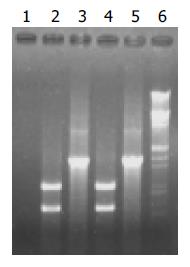
Figure 4 DNA detection of transformants by PCR amplifica-tion and PstI digested PCR products.
Lane 1: control for PCR; lane 2: PstI digesting product of lane 3; lane 3: PCR detection of C. glutamicum KM; lane 4, PstI digesting product of lane 5; lane 5: PCR detection of C. glutamicum GAK; lane 6: Markers, EcoRI/Hind III digesting λ phage DNA.
Figure 5 Auxanogram detection of C.
glutamicum (Tyr-). MM: C. glutamicum GAK on MM; Tyr: C.glutamicum GAK on MM + Tyr; Phe: C.glutamicum GAK on MM + Phe; Trp: C.glutamicum GAK on MM + Trp.
-
Citation: Liu DX, Fan CS, Tao JH, Liang GX, Gao SE, Wang HJ, Li X, Song DX. Integration of
E .coli aroG-phe A tandem genes intoCorynebacterium glutamicum tyr A locus and its effect on L-phenylalanine biosynthesis. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(24): 3683-3687 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i24/3683.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i24.3683